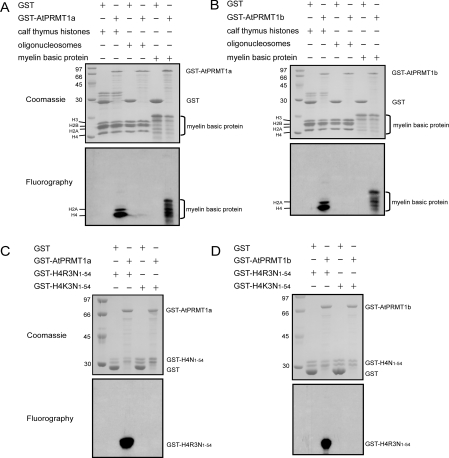
Figure 2. Methyltransferase activities and site specificity of AtPRMT1a and AtPRMT1b in vitro.
Methyltransferase activities of AtPRMT1a (A) and AtPRMT1b (B). GST, GST–AtPRMT1a or GST–AtPRMT1b was immobilized on glutathione–Sepharose beads and incubated with indicated substrates: calf thymus histones, oligonucleosomes and myelin basic protein in the presence of [3H]SAM for 1 h in a final volume of 30 μl of HMT buffer (20 mM Tris/HCl, 4 mM sodium EDTA, 1 mM PMSF and 1 mM dithiothreitol). Methylated proteins were separated by SDS/15% PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (A and B, upper panels) and visualized by fluorography (A and B, lower panels). The corresponding proteins are indicated alongside the panels, and molecular masses are indicated in kDa. Both AtPRMT1a (C) and AtPRMT1b (D) specifically methylate histone H4 at R3. Two forms of recombinant histone H4 (GST–H4R3N1–54 and GST–H4K3N1–54) were generated as substrates for AtPRMT1a and AtPRMT1b, and were subjected to the arginine methylation assay as described in the Experimental section. After the reaction, the proteins were separated by SDS/15% PAGE and stained by Coomassie Blue (C and D, upper panels) and visualized by fluorography (C and D, lower panels). The corresponding proteins are indicated on the right of each panel, and molecular masses are indicated on the left in kDa.