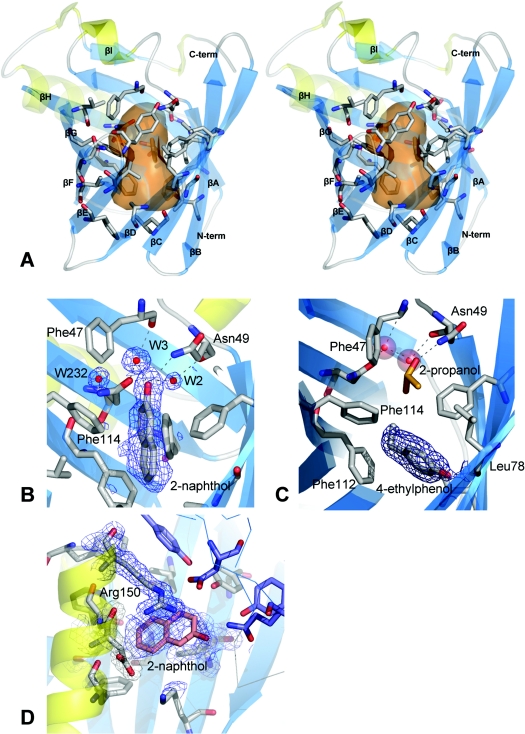
Figure 2. Trichosurin structure, topology and ligand binding.
(A) Stereo diagram showing the trichosurin monomer, with β-strands in blue (labelled βA–H) and α-helices yellow. The residues whose side chains define the binding pocket are rendered as grey sticks with oxygen atoms in red and nitrogen in blue. The transparent orange surface represents the approximate size of the internal cavity as a molecular contact surface described by a sphere of 1.4 Å radius. (B) A 2(Fo)−(Fc) electron density map contoured at 1σ depicted in blue mesh showing the 2-naphthol ligand bound within the trichosurin barrel and the hydrogen bonds made to water W3 and Asn49 ND1. (C) 2(Fo)−(Fc) electron density map contoured at 1σ showing 4-ethylphenol (surrounded by electron density mesh) donating a hydrogen bond to Leu78 O and occupying the lower part of the trichosurin-binding pocket. A 2-propanol molecule (orange and red) is still bound in the upper part of the binding pocket along with the water molecules W2 and W3 (red spheres). (D) The second binding site for 2-naphthol between the helix, the outside of the barrel and the dimer interface. The blue mesh is from a 2(Fo)−(Fc) electron density map contoured at 1σ. The thin blue lines and the purple residues are from the second molecule of the dimer.