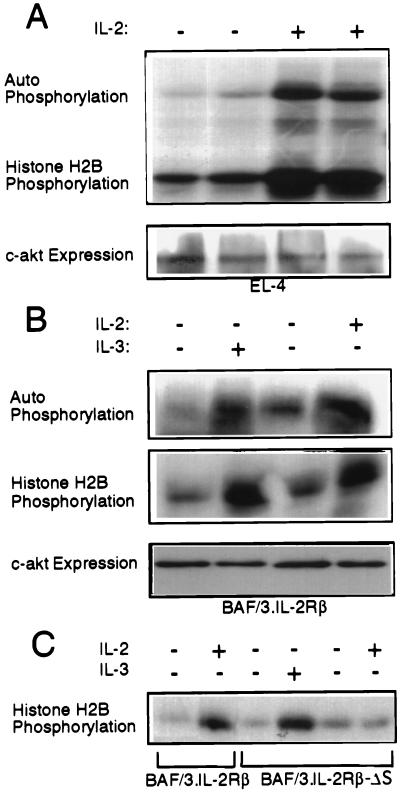
Figure 1.
Akt is activated by IL-2 and IL-3 in EL4·IL-2 cells and BAF/3 cells expressing IL-2Rβ, but not IL-2Rβ·ΔS. (A) Five × 106 EL4·IL-2 (ATCC, TIB 181) cells, cultured at a concentration of 0.5 × 106 cells per ml, were serum-starved for 16 h. Some of the starved cultures then were stimulated with IL-2 (100 units/ml) for 10 min as indicated. (Upper) In vitro kinase assays of Akt immunoprecipitated from Nonidet P-40 lysates of unstimulated or IL-2-stimulated EL4 cells, using the anti-Akt-CT antibody. (Lower) Anti-Akt-CT Western blot of the immunoprecipitates used in the kinase assay above. (B) Five × 106 BAF/3 cells stably transfected with the expression construct pdKCR-IL-2Rβ (3) cultured at a concentration of 0.5 × 106 cells per ml, were starved of IL-3 for 16 h. (Top and Middle) In vitro kinase assays carried out on anti-Akt immunoprecipitates of unstimulated and IL-2 (100 units/ml) or IL-3 (50 units/ml) stimulated cell lysates. (Bottom) Expression of c-akt as determined by probing Western blots of total cell lysates with the anti-Akt-CT antibody. (C) BAF/3 cells (5 × 106) stably expressing the IL-2Rβ or the IL-2Rβ·ΔS mutant, cultured at the concentration of 0.5 × 106 cells per ml, were transiently transfected with HA·Akt. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were starved of IL-2 and IL-3 for 16 h. Subsequently, they were stimulated with IL-2 or IL-3 for 10 min as indicated. In vitro kinase assays were carried out on HA[A0]Akt immunoprecipitated from Nonidet P-40 cell lysates.