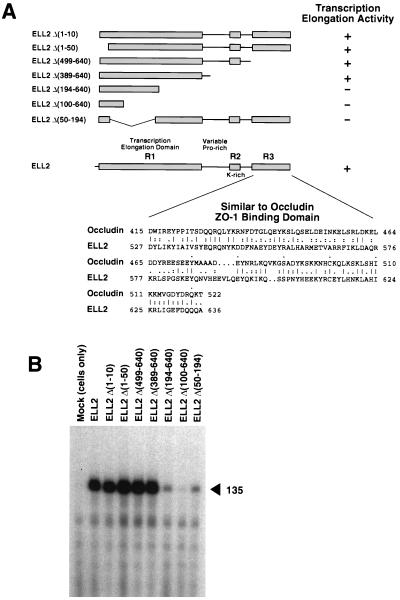
Figure 4.
Localization of the ELL2 elongation activation domain. (A) Summary of ELL2 mutants and their activities in transcription. Wild-type ELL2 is diagrammed at the bottom of the panel. Conserved regions 1, 2, and 3 (R1, R2, and R3) are indicated by the shaded boxes. The alignment of region 3 with the C-terminal ZO-1 binding domain of occludin was generated with the bestfit program of the Genetics Computer Group package, using the symbol comparison table of Gribskov and Burgess (34). (B) Wild-type ELL2 and ELL2 mutants were expressed in E. coli and purified by nickel-affinity chromatography as described (13). Approximately 50 ng of each protein (in a maximum volume of 50 μl) was renatured and assayed as described (13) for its ability to stimulate synthesis of the 135-nucleotide transcript from the T-less cassette of oligo(dC)-tailed template pCpGR220 S/P/X. Reactions containing ≈0.01 unit of RNA polymerase II, 100 ng template, and the indicated ELL2 proteins were incubated at 28°C for 5 min in the presence of 50 μM ATP, 50 μM GTP, 1.8 μM CTP, and 10 μCi of [α-32P]CTP. The control reaction (MOCK) contained an identically prepared fraction from uninfected JM109(DE3) cells.