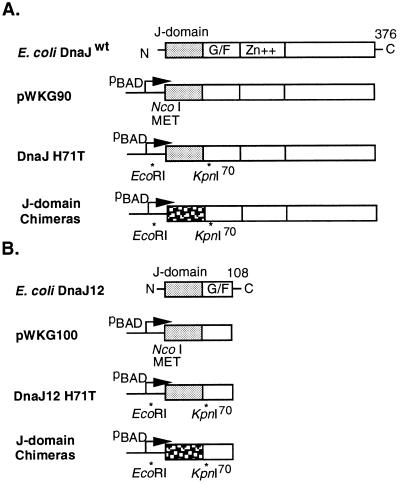
Figure 2.
Construction of J-domain PCR replacement chimeras. (A) Plasmids derived from the dnaJ wild-type (dnaJwt) clone. Four domains comprising the N-terminal J-domain, glycine-phenylalanine rich region (G/F), Zn+ finger domain, and a less conserved C-terminal domain are shown (11). (B) Plasmids derived from a dnaJ12 clone that lacks all coding sequence beyond residue 108. A phenotypically neutral mutation was introduced (H71T) that generated a unique KpnI site at the end of the J-domain. Viral T/t exons were PCR amplified to introduce the appropriate EcoRI and KpnI sites. The J-domain is shown stippled and proximal to the pBAD promoter used for conditional expression.