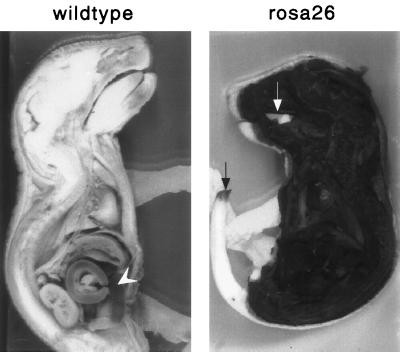
Figure 1.
Ubiquitous expression of β-gal in newborns. A wild-type (Left) and a heterozygous (Right) newborn were fixed with paraformaldehyde and cross-sectioned prior to X-Gal staining. The arrowhead indicates background staining in the intestines. The white arrow indicates the tongue, in which the mucus membrane prevented penetration of the X-Gal stain. The black arrow shows the depth of X-Gal penetration from the cut surface in the tail. Note that skin makes a good barrier.