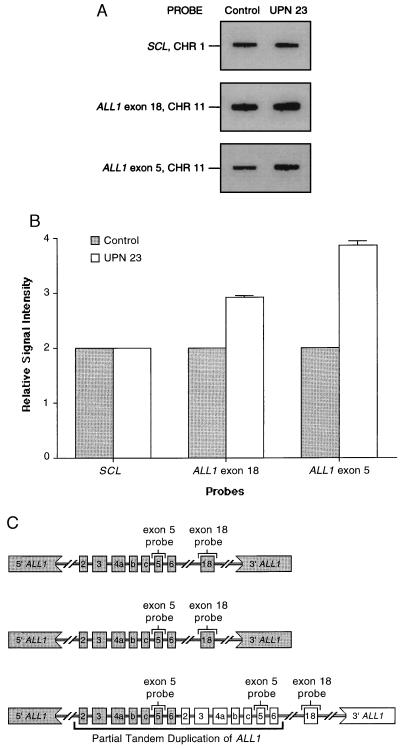
Figure 1.
Dosage of the wild-type and partially duplicated ALL1 alleles in AML blasts of a patient (UPN 23) with +11 as a sole cytogenetic abnormality. (A) The pattern obtained with hybridization using SCL, ALL1 exon 18, and ALL1 exon 5 probes. The signal intensity detected with the SCL probe from chromosome 1 was the same for the normal control and UPN 23 (see Table 1), indicating that equivalent amounts of DNA were loaded. However, the signal intensity for the ALL1 exon 18 and the ALL1 exon 5 are visibly different when comparing the equal amounts of DNA from the normal control and UPN 23. (B) Graphical depiction of the quantitative phosphorimage analysis of signal intensity from SCL, ALL1 exon 18, and ALL1 exon 5 blots shown in A. Each measurement is relative to one-half the signal intensity in the normal donor using the same probe. This shows that UPN 23 with +11 had three copies of ALL1 exon 18 that is outside the duplication, but four copies of ALL1 exon 5 that is within the duplication. (C) A schematic diagram of ALL1 allelic dosage in AML with +11 and the partial duplication, incorporating data obtained above. This shows that the three copies of ALL1 exon 18 and four copies of ALL1 exon 5 can be accounted for with only one of three chromosomes containing the partial tandem duplication of ALL1. The two remaining chromosomes 11 each contain a wild-type ALL1 allele.