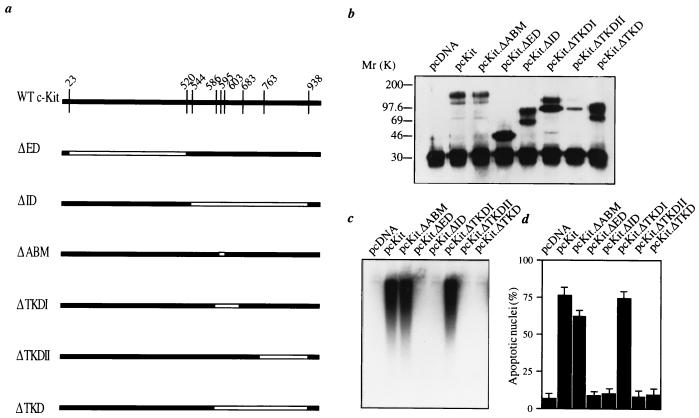
Figure 3.
Induction of apoptosis by c-Kit requires an intact tyrosine kinase domain. (a) Schematic diagram of c-Kit deletion mutants (ΔED, extracellular domain; ΔID, intracellular domain; ΔABM, ATP-binding motif ΔTKDI, tyrosine kinase domain I; ΔTKDII, tyrosine kinase domain II; ΔTKD, entire tyrosine kinase domain). (b) Expression of c-Kit mutants. Each plasmid at 20 μg was transfected into 293 cells by the calcium phosphate method. Immunoprecipitation of 500 μg of cellular protein followed by Western blotting with anti-c-Kit was performed at 48 h after transfection. (c and d) Induction of apoptosis by c-Kit mutants. Each plasmid at 2.5 μg was transfected into U87 cells as in Fig. 2. The cytoplasmic DNA fragmentation assay (c) and quantitation of apoptosis (d) were performed at 48 h after transfection as in Fig. 2 b–d. Data in d are the means ± SD for duplicate determinations. Results were similar in two or three experiments.