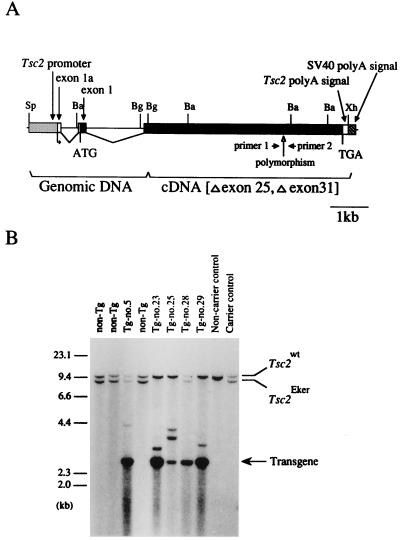
Figure 1.
Generation of the transgenic founders. (A) Structure of the wild-type Tsc2 gene used in this study. Closed and opened boxes indicate coding and noncoding regions of the Tsc2 gene lacking exons 25 and 31 due to alternative splicing, respectively. Hatched and striped boxes indicate the Tsc2 promoter region and the SV40 DNA fragment containing the poly(A) addition signal, respectively. Positions of the translational initiation (ATG) and termination (TGA) codons, polymorphic sequence, and primers for RT-PCR analysis are noted below. Sp, SpeI; Ba, BamHI; Bg, BglII; Xh, XhoI. (B) Southern blot analysis of the transgenic founders. BamHI-digested DNA samples from five transgenic founders (Tg-no.5, no.23, no.25, no.28, and no.29), three nontransgenic littermates (non-Tg), an Eker carrier, and noncarrier controls were probed with a 32P-labeled rat Tsc2 cDNA fragment covering exons 21–27. Band positions of the endogenous wild-type Tsc2 allele (Tsc2wt), the endogenous germ-line mutant Tsc2 allele (Tsc2Eker), and the Tg are indicated on the right. Positions of size markers (λ/HindIII fragments) are shown on the left.