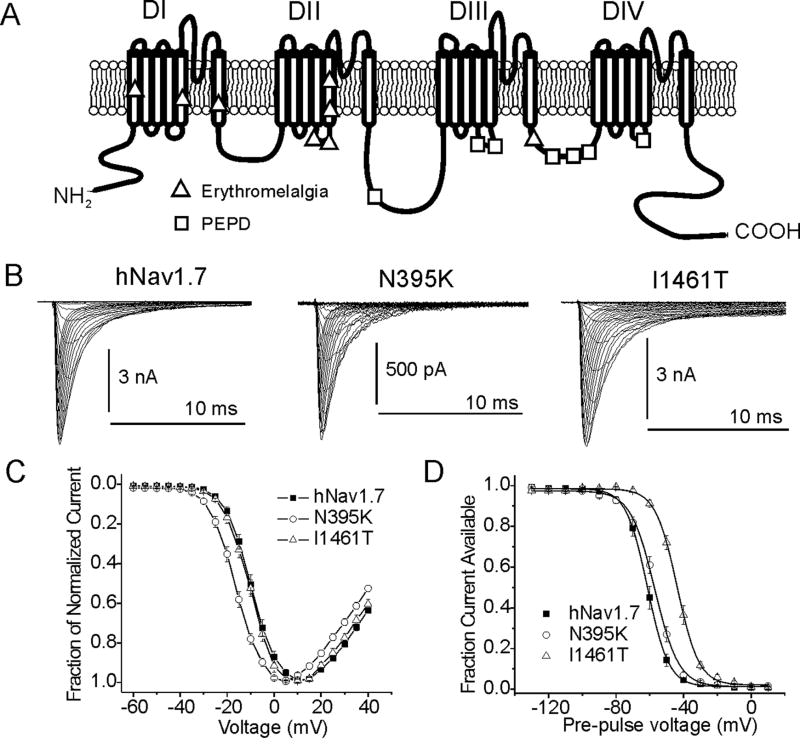
Figure 3.
A, Linear diagram of a Nav1.7 voltage-gated sodium channel showing locations of single point-mutations indicated in the painful neuropathies erythromelalgia and Paroxymsal Extreme Pain Disorder (PEPD). B, Na+ current traces from the wild-type human Nav1.7 channel and from Nav1.7 channels containing an erythromelalgia mutation (N395K) and a PEPD mutation (I1461T). C, Current-voltage (IV) profile for wild-type, N395K, and I1461T Nav1.7 channels. All erythromelalgia mutations cause a hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage-dependence of activation for Nav1.7 channels while PEPD mutations thus far show no effects on activation. D, Steady-state fast inactivation profile for wild-type, N395K, and I1461T Nav1.7 channels. PEPD mutations cause a depolarizing shift in the voltage-dependence of steady-state fast inactivation while erythromelalgia mutants have little or no effect on fast inactivation properties.