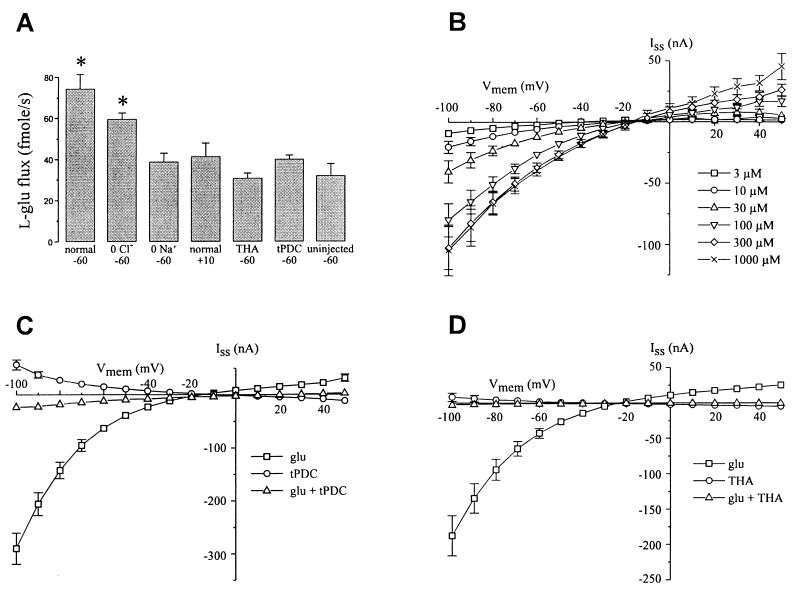
Figure 3.
Pharmacology of EAAT5-mediated uptake and currents. (A) Uptake of [3H]-l-glutamate (100 μM) in oocytes voltage-clamped at −60 mV in normal Ringers solution (96 mM NaCl) (normal) or sodium-free (0 Na+) or chloride-free Ringers (0 Cl−) or voltage-clamped at +10 mV in normal Ringers. Uptake was sodium- and voltage-dependent. Additionally, uptake (−60 mV, normal Ringers) was blocked by coapplication of 100 μM THA or tPDC. ∗, Differs significantly from uptake measured in control uninjected oocytes. Data are the average of five cells each. (B) Dose- and voltage-dependent steady-state currents due to the application of l-glutamate to EAAT5-expressing oocytes. Concentration of l-glutamate indicated in the legend. Data are the average of seven cells. (C) Steady-state current elicited by 100 μM l-glutamate (squares) is blocked by coapplication of 100 μM tPDC (triangles); 100 μM tPDC alone (circles) elicits a small outward current at hyperpolarized potentials. Data are the average of four cells. (D) Steady-state current elicited by 100 μM l-glutamate (squares) is blocked by coapplication of 100 μM THA (triangles); 100 μM THA alone (circles) elicits a small outward current at hyperpolarized potentials. Data are the average of six cells. All error bars represent SEM. Error bars smaller than the symbols are not shown.