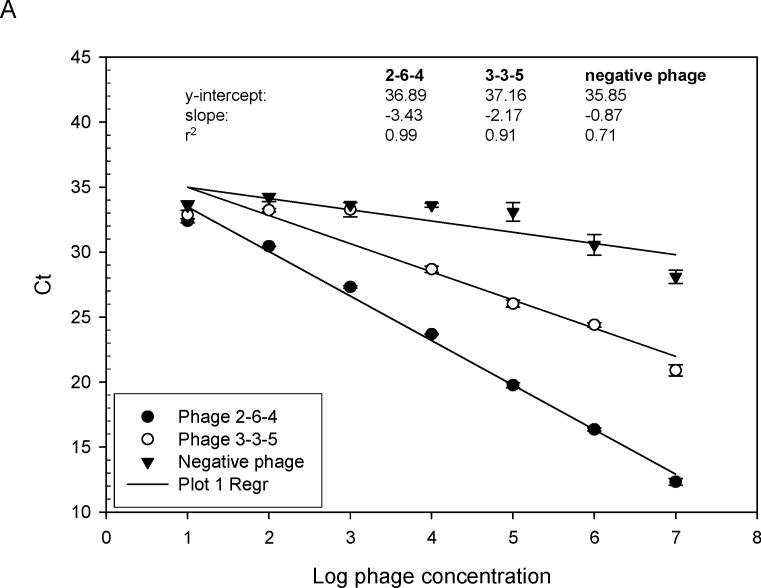
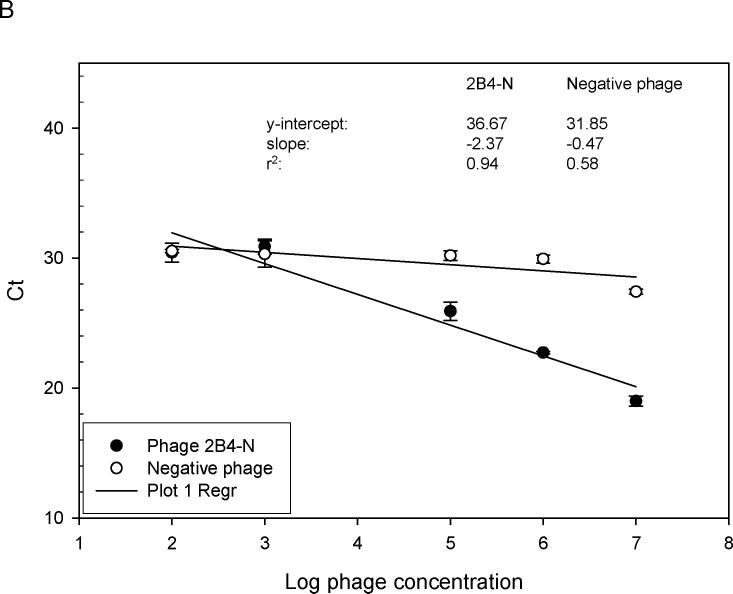
Fig. 4.
Relative binding affinity of rAbs to phage using RT-IPCR. (A). MS rAbs #37 and #52 were coated onto wells of ELISA plates overnight at 4°C. Ten-fold serial dilutions of phage 2−6−4 (previously shown to be specific for rAb #37) and an irrelevant phage were added to wells containing rAb #37; 10-fold serial dilutions of phage 3−3−5 (previously shown to be specific for rAb #52) were added to wells containing rAb #52. Phage binding was determined by (RT) PCR. High-affinity rAb #37 had lower Ct values (slope = −3.43) than the lower affinity rAb #52 (slope = −2.17), and the negative control phage had the highest Ct values (slope = −0.87). B. SSPE rAb 2B4 binding to phage 2B4-N (previously shown to be specific for 2B4-N). High-affinity 2B4 had a lower Ct value (slope = −2.37) compared to the negative control phage with high Ct value (slope = −0.47). Error bars represent standard deviation of duplicate samples.