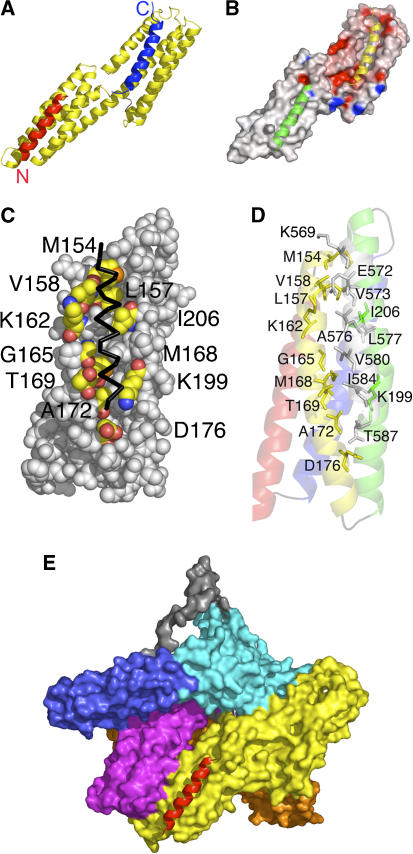
Figure 1.
The crystal structure of human vinculin bound to Shigella's IpaA-VBS2. (A) Cartoon representation of vinculin (Vh1, residues 1–258, yellow) bound to two IpaA-VBS2 molecules (red and blue). The binding of IpaA-VBS2 (blue) to the N-terminal helical bundle of Vh1 causes helical bundle conversion from a four-helical vinculin bundle to a five-helical bundle, and is very similar to the structures that have been observed for the binding of talin's or α-actinin's VBSs to Vh1 (Izard et al, 2004; Izard and Vonrhein, 2004; Papagrigoriou et al, 2004; Bois et al, 2005, 2006; Fillingham et al, 2005; Gingras et al, 2006). The C-terminus of IpaA-VBS2 is indicated. The binding of a second IpaA-VBS2 (red) to the C-terminal helical bundle is unprecedented and its binding rather occurs via a helix addition mechanism. The N- and C-termini of IpaA-VBS2 are indicated. (B) Electrostatic surface potential (red, negative; blue, positive) of <−20 to >+20 kbT e−1, where kb is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature of the Vh1 structure in its IpaA-VBS2-bound state. IpaA-VBS2 bound to the N-terminal or C-terminal helical bundles are shown as a cartoon in yellow and green, respectively. (C) View of the surface vinculin residues (labeled; carbon, yellow; oxygen, red; nitrogen, blue; sulfur, orange) of the C-terminal helical bundle of Vh1 in contact with IpaA-VBS2 (back, Cα trace). (D) Cartoon representation of the C-terminal helical bundle of Vh1 (residues 130–150, red; 154–181, yellow; 185–218, green; 223–251, blue) in complex with IpaA-VBS2 (gray). Residues involved in binding are labeled. (E) Superposition of the C-terminal helical Vh1 bundle of the Vh1:IpaA-VBS2 structure onto the full-length structure of vinculin in its inactive conformation (PDBID 1TR2; Borgon et al, 2004) reveals no changes in the structure of this bundle upon binding to IpaA-VBS2, and also establishes that this new binding site is exposed; therefore, IpaA can bind to a conformation reminiscent of inactive vinculin. Vinculin domains Vh1, Vh2, Vh3, Vt2, and Vt are colored in yellow, orange, magenta, blue, and cyan, respectively, and the disordered proline-rich region was modeled and is shown in gray. IpaA-VBS2 bound to the C-terminal helical bundle of Vh1 is shown in red.