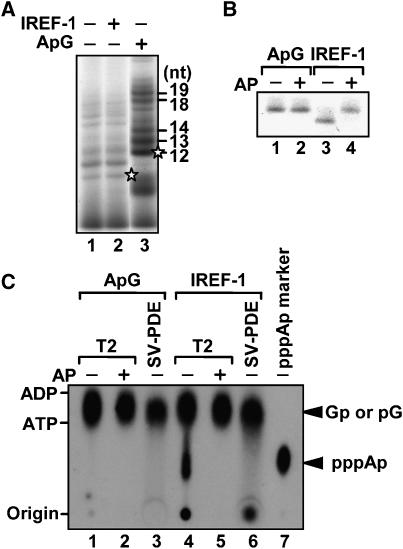
Figure 2.
Detection of 5′ triphosphate end group. (A) Limited elongation assays. Limited elongation assays were carried out in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) or presence (lane 3) of ApG with (lane 2) or without (lanes 1 and 3) IREF-1. (B) Alkaline phosphatase treatment of limited elongation products. Limited elongation products (indicated by asterisks in panel A) synthesized in the presence of ApG (lanes 1 and 2) or IREF-1 (lanes 3 and 4) were excised from gel, and treated with (lanes 1 and 3) or without (lanes 2 and 4) alkaline phosphatase (AP). (C) Detection of pppAp using thin-layer chromatography. Twelve nucleotide long of limited elongation products in the presence of ApG (lanes 1–3) or IREF-1 (lanes 4–6) were excised from gel, and treated with RNase T2 (lanes 1, 2, 4, 5, and 7) or SV-PDE (lanes 3 and 6). Products were separated through thin-layer chromatography with 1.6 M LiCl, and visualized by autoradiography. Alkaline phosphatase-treated limited elongation products (AP; lanes 2 and 4) and RNA synthesized by T7 RNA polymerase in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP (lane 7) were used as control products.