Figure 7.
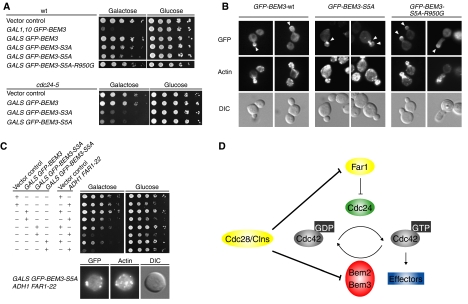
Phosphorylation of Bem3p contributes to cellular polarization at bud emergence, but does not regulate its polarized localization. (A) Five-fold serial dilutions of an equal number of wild-type (upper panel; K699) or cdc24-5 (lower panel; yMG313) cells transformed with a control vector (pRS415, GAL1,10) or plasmids allowing as indicated overexpression of GFP-Bem3p (pYS417 and pMK61), GFP-Bem3p-S3A (pMK70), Bem3p-S5A (pMK91), GFP-Bem3p-R950G (pYS418) or GFP-Bem3p-S5A-R950G (pMK101) from the inducible GAL1,10 or GALS promoter, were spotted on media containing galactose (GAL promoter on) or glucose (GAL promoter off). The plates were photographed after 3 days at 25°C. (B) The localization of GFP-Bem3p (pMK61), GFP-Bem3p-5A (pMK91) and GFP-Bem3p-5A-R950G (pMK101) expressed in wild-type (K699) cells from the inducible GALS or GAL1,10 promoter, respectively, was analyzed by GFP microscopy (upper row). Polarized actin was stained with rhodamine-labeled phalloidin (actin, middle row), and DIC microscopy (lower row) shows the morphology of the analyzed cells. Arrowheads mark the localization of the GFP fusion proteins at tips of small buds. (C) Five-fold serial dilutions of an equal number of wild-type (K699) cells transformed with a combination of plasmids allowing as indicated overexpression of GFP-Bem3p (pYS417), GFP-Bem3p-S3A (pMK70) or GFP-Bem3p-S5A (pMK91) from the inducible GALS and Far1p-22 (pYS82) from the ADH1 promoter (or respective control vectors). The cells were spotted on media containing galactose (GAL promoter on) or glucose (GAL promoter off) and photographed after 3 days at 25°C. (D) We propose that the Cdc42p-GAPs Bem2p and Bem3p prevent premature activation of Cdc42p during the G1-phase of the cell cycle. Upon cellular polarization, the G1-CDK Cdc28p/Cln phosphorylates and inhibits Bem2p and Bem3p activity, thereby promoting the formation of a stable polarity axis by lowering the threshold for Cdc42p activation. In haploid cells, Cdc28p/Clnp also triggers degradation of nuclear Far1p, thereby releasing Cdc24p into the cytoplasm. Cdc28p-Cln kinase thus promotes bud emergence by phosphorylating both positive and negative regulators of Cdc42p.