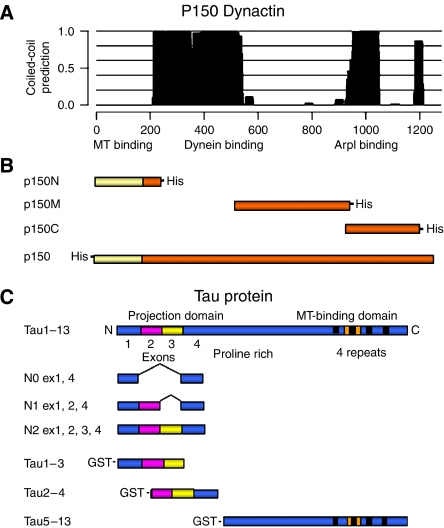
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of dynactin p150 functional domains and dynactin p150 and tau DNA fragments used for in vitro experiments. (A) p150 functional domains and associated coiled-coil domains (plot); dynein- and ARP1-binding domains overlap with two main coiled-coil domains in the protein structure; a small coiled-coil domain is present near the C-terminus, around aa 1200, overlapping with the tau-interacting region identified in this work. (B) His-tagged N-terminal (p150N; aa 1–210), central (p150M; aa 550–940), C-terminal (p150C; aa 900–1200) and full-length p150 used for in vitro binding experiments. (C) The 441-amino-acid isoform of human brain tau (htau40, exons 1–13) contains a C-terminal MT-binding domain with 4 repeats (black boxes) one of which (encoded by exon 10, indicated in orange) is missing from tau isoforms with three repeats. The N-terminus contains alternatively spliced exon 2 (magenta) and exon 3 (yellow). Full-length tau1–13 and fragments N0, N1 and N2 were used in the bacterial two-hybrid screening. Tau1–13 and GST-tagged tau1–3, tau2–4 and tau5–13 constructs were used for in vitro binding experiments.