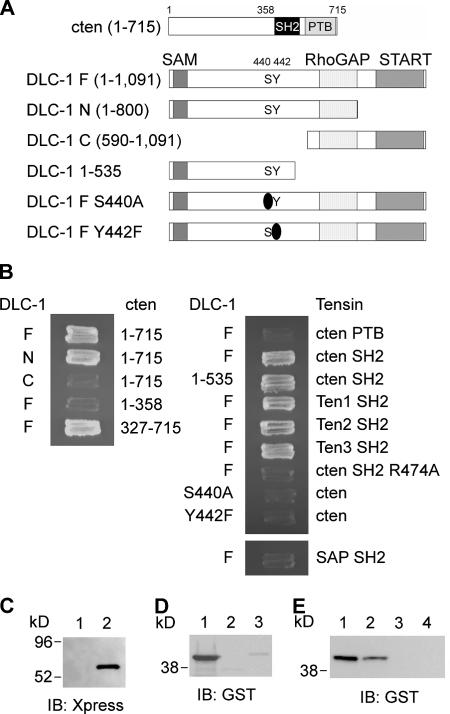
Figure 2.
Determination of binding regions on cten and DLC-1 and their binding specificities. (A) Schematic diagram of cten and DLC-1 and their segments that were used for mapping the binding sites. (B) AH109 yeast cells transformed with the indicated plasmids and grown on two-dropout plates were restreaked on four-dropout plates. (C) Bacterial lysates containing Xpress–DLC-1 (113–535) were incubated with immobilized GST (lane 1) or GST-cten SH2 (lane 2). After washing, the associated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Xpress antibody. (D) 0.5 μg of purified GST-cten SH2 (lane 1), GST-Src SH2 (lane 2), and GST-p85 SH2 (lane 3) recombinant proteins were incubated with DLC-1 peptide (CSRLSIY442DNVPG) immobilized on agarose beads. After washing, the associated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody. (E) 0.5 μg of purified GST-cten SH2 recombinant proteins were incubated with DLC-1 peptide (CSRLSIY442DNVPG; lane 1), tyrosine-phosphorylated DLC-1 peptide (CSRLSIpY442DNVPG; lane 2), EGFR peptide (CSVQNPVY1086HNQP; lane 3), or tyrosine-phosphorylated EGFR peptide (CSVQNPVpY1086HNQP; lane 4) immobilized on agarose beads. After washing, the associated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody.