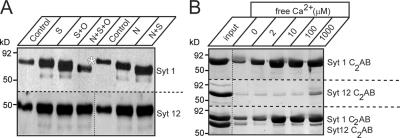
Figure 3.
Synaptotagmin-12 is not glycosylated and lacks phospholipid binding. (A) Deglycosylation analysis of synaptotagmin-12. Proteins from rat brain homogenate were treated with sialidase (S), o-glycanase (O), PNGase (N), or different combinations of these enzymes to remove neuraminic acid and O- and N-linked sugars. The samples were then analyzed by immunoblotting with the antibodies to synaptotagmin-1 and -12. Treatment with deglycosylation enzymes results in a substantial change in mobility of synaptotagmin-1 in SDS-PAGE, but has no effect on mobility of synaptotagmin-12, indicating that synaptotagmin-12 is not glycosylated. (B) C2 domains of synaptotagmin-12 do not bind phospholipids in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Recombinant C2AB domains of synaptotagmins-1 and -12 were expressed as GST-fusion proteins and tested in phospholipid-binding assay at different concentrations of free Ca2+ (as indicated on the top of the gel). Unlike C2 domains of synaptotagmin-1 (Syt 1 C2AB; top), C2 domains of synaptotagmin-12 (Syt 12 C2AB) do not bind phospholipids when tested alone or in the presence of Syt 1 C2AB.