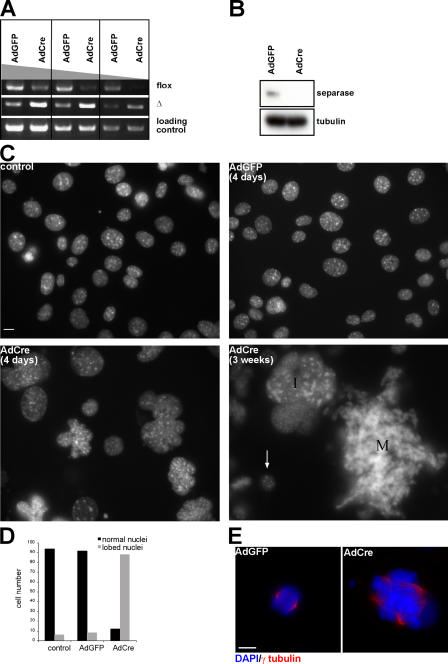
Figure 4.
iMEFs lacking Separase become polyploid with multipolar spindle. (A–E) Separase Δ/flox iMEFs were infected with AdCre and -GFP, respectively. (A) Genomic PCR was performed to reveal the deletion of the last eight exons in the Separase genomic locus 4 d after virus infection. PCR primers were used to amplify the flox and the deletion allele. The region located in the Separase NH2-terminal coding sequence was amplified for loading control. (B) Western blot analysis of Separase protein level in the cells 4 d after viral infection. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (C) Nuclear morphology revealed by DAPI staining. Control represents Separase Δ/flox iMEFs not infected with the virus. iMEFs were infected with AdGFP and -Cre, respectively, and DAPI staining was performed 4 d later. Note that the size of the cells 3 wk after AdCre transduction can be directly compared with small nuclei from cells that were most likely not infected with the virus (arrow). I, interphase cell; M, mitotic cell. (D) Number of lobed nuclei 4 d after viral infection counted in 100 interphase cells. (E) Immunofluorescence staining of the cells 3 d after viral infection. γ-tubulin was used to stain the spindle. Bars, 10 μm.