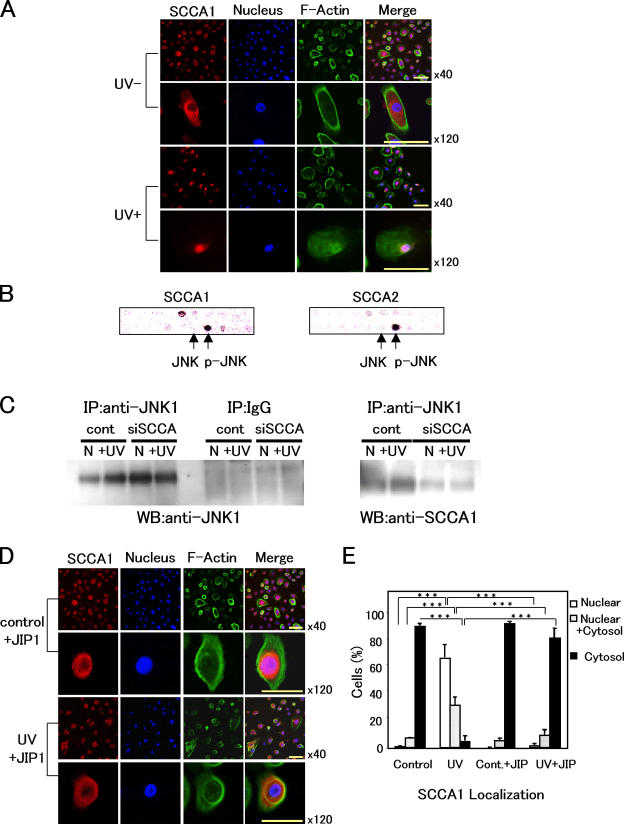
Figure 3.
SCCA1 binds with JNK1 and translocates into nucleus after UV irradiation. (A) Localization of SCCA1 before and 24 h after UV irradiation (50 mJ/cm2). NHK cells were stained for SCCA1, nucleus, and F-actin with (UV+) or without UV treatment (UV−). (B) Interaction of SCCAs with p-JNK. HSC-4 cell extract was applied to a signal transduction antibody array, followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated antibody against either SCCA1 or SCCA2. Black spots indicate positive binding to p-JNK. Arrows indicate the spots representing antibodies to JNK and p-JNK. (C) HaCaT cell extracts transfected with control pSilencer vector or siSCCA were immunoprecipitated with anti-JNK1 antibody, followed by blotting with indicated antibodies. Normal rabbit IgG was used as a nonspecific control (middle). Effects of UV irradiation were also examined (N, not irradiated; +UV, 5 min after 100 mJ/cm2 UV irradiation). (D) Effects of JIP1 peptide on SCCA1 localization. NHK cells were cultured in the presence of 5 μM of JIP1 peptide and stained for SCCA1, nucleus, and F-actin with (UV+, 50 mJ/cm2) or without (UV−) UV treatment. (E) Statistical analysis of SCCA1 translocation. In each case (i.e., control [nontreated], UV-irradiated [UV], control + JIP1 peptide [5 μM; Cont. + JIP], and UV-irradiated [50 mJ/cm2] + JIP1 peptide [5 μM; UV + JIP]), a minimum of 300 cells were counted three times. Error bars represent the mean of three experiments ± SD. ***, P < 0.001. Bars, 20 μm.