Figure 5.
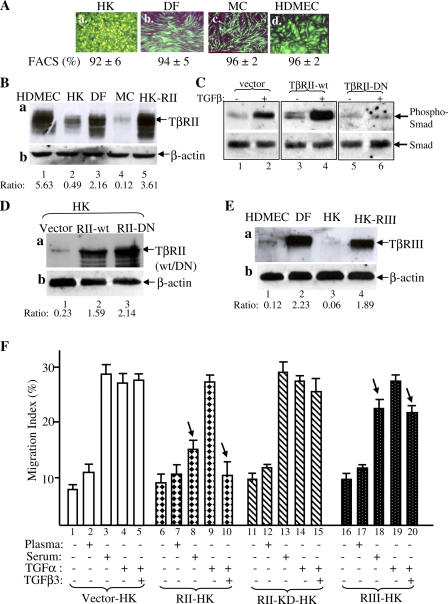
Up-regulation of TβRII converts epidermal HK motility to become TGFβ3 sensitive just like dermal cells. (A) Lentiviral infection offered >90% gene transduction efficiency in DFs, MCs, HDMECs, and HKs. 48 h after infection with pRRLsin-CMV-EGFP, the plates were analyzed under fluorescence microscopy and photographed. The cells were suspended by trypsin and subjected to FACS analyses for measurement of the gene transduction efficiency (percentage of green cells/total cells). (B) Elevated expression of TβRII in HKs after pRRLsin-TβRII infection (lane 5) in comparison with the endogenous TβRII expression in HKs (lane 2), DFs (lane 3), and HDMECs (lane 1). Equal amounts of cell extracts of the indicated cell types were blotted with anti-TβRII antibody (a) or anti–β-actin antibody (b). (C) TβRII-KD blocks TGFβ3-stimulated Smad2/3 phosphorylation in HKs. The HKs, infected with vector, wild-type TβRII, or TβRII-KD, were untreated or treated with 2.5 ng/ml TGFβ3 for 45 min and analyzed for the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 similar to the assays shown in Fig. 4 (C and D). (D) Elevated expression of TβRII-KD in HKs after pRRLsin-CMV–TβRII-KD infection (lane 3) in comparison with elevated wild-type TβRII expression (lane 2) and the endogenous TβRII expression in HKs (lane 1). (E) Elevated expression of TβRIII in HKs (lane 4 vs. lane 3) after pRRLsin-CMV-TβRIII infection in comparison with endogenous TβRIII expression in DFs (lane 2) and HDMECs (lane 1). (F) The aforementioned TβR-engineered HKs were tested for their migratory responses to plasma, serum, or TGFα with or without 0.5 ng/ml TGFβ3 in colloidal gold migration assays. MIs are shown. This experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent SEM.