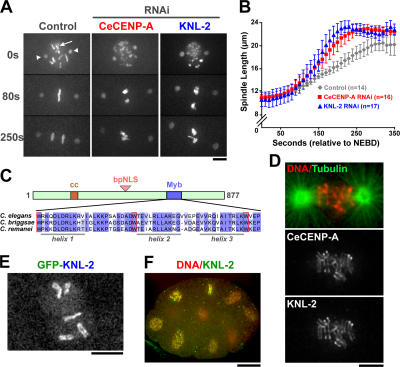
Figure 1.
KNL-2 is a novel Myb domain protein whose depletion results in a CeCENP-A loss of function phenotype. (A) Images of control, CeCENP-A, and KNL-2–depleted embryos expressing GFP-histone H2b (arrow) to mark chromosomes and GFP–γ-tubulin (arrowheads) to mark the spindle poles. Time is given in seconds relative to nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD). (B) Spindle pole separation kinetics in control, CeCENP-A depletion, and KNL-2 depletion. Error bars represent the SEM with a confidence interval of 0.95. (C) Primary sequence features of KNL-2. The divergent Myb domain (amino acids 624–677) is shown on the bottom for C. elegans, C. briggsae, and C. remanei KNL-2. The predicted helical secondary structure is shown under the sequences, and the conserved tryptophan (W) residues are boxed in red. (D) KNL-2 and CeCENP-A colocalize at kinetochores during mitosis. (E) GFP–KNL-2 exhibits kinetochore localization. (F) KNL-2 localizes to kinetochores in later embryonic divisions. A multicellular embryo in which DNA (red) and KNL-2 (green) are labeled is shown. Bars (A, D, and E), 5 μm; (F) 10 μm.