Figure 1.
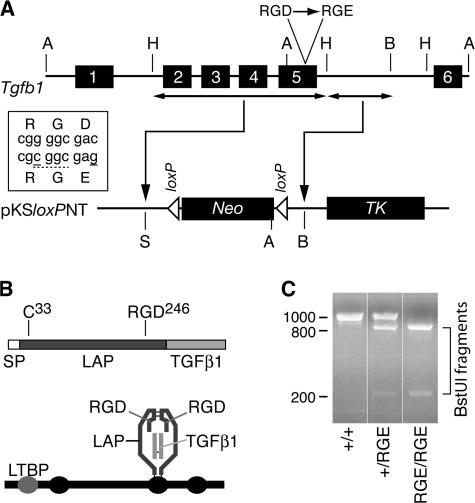
Generation of mice with a targeted mutation of Tgfb1. (A) Schematic of Tgfb1 (top) and fragments thereof used for insertion in targeting vector (bottom). Box shows mutations (solid underlines) introduced in exon 5 to encode a BstUI restriction site (dashed underline) and the D-to-E mutation. Restriction sites: A, ApaI; B, BamHI; H, HindIII; S, SalI. Neo, neomycin resistance cassette; TK, thymidine kinase cassette. (B) The TGFβ1 mRNA encodes a protein sequence consisting of a signal peptide (SP), propeptide (LAP), and the TGFβ1 cytokine (top). The integrin-binding motif RGD is near the C terminus of LAP. The processed latent factor consists of noncovalently associated disulfide-linked homodimers of the LAP and TGFβ1 monomers (bottom). LAP can be disulfide linked via cys-33 to one of the cysteine-repeat domains (ovals) of LTBP-1, -3, or -4. (C) PCR genotyping results from Tgfb1+/+, Tgfb1+/RGE, and Tgfb1RGE/RGE mice.