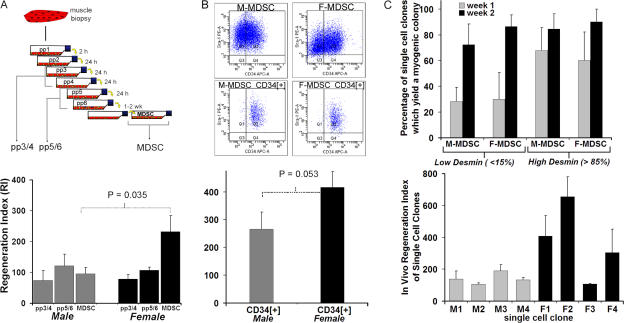
Figure 4.
Examination of alternate M-MDSC sources. (A) The preplate technique to isolate subfractions of muscle-derived cells is based on their adhesion characteristics from muscle biopsy. Male myoblast subfractions also demonstrated low regeneration efficiency. There was no significant difference between the RIs of male pp3/4 (74 ± 32; n = 4) and pp5/6 (122 ± 38; n = 3) when compared with the RI of M-MDSCs (109 ± 18; n = 10 for all M-MDSC populations shown in Fig. 2). There also was no significant difference between the RIs of male myoblasts and female myoblasts (female pp3/4 RI = 79 ± 14, n = 4; female pp5/6 RI = 107 ± 10, n = 3; P > 0.05). The bars for the M- and F-MDSCs represent the mean RIs for all male and female populations shown in Fig. 2 (95 ± 21 [n = 10] and 230 ± 52 [n = 15], respectively). (B) M- and F-MDSCs were sorted by FACS to obtain a subpopulation expressing the stem cell marker CD34. The presorted population had similar expression levels for desmin/Sca-1 and CD34. Cells were purified to contain >96% CD34+ cells only. Transplantation of purified M-MDSCs expressing CD34 resulted in a significantly lower RI (266 ± 61) than did transplantation of F-MDSCs expressing CD34 (417 ± 56; P = 0.052; t test). All RIs are reported as means ± SEM (error bars), and p-values are for t test comparisons. (C, top) 2 wk after single-cell cloning, there was no significant difference in the percentage of single-cell clones derived from M- or F-MDSC populations that yielded myogenic colonies as defined by myotube formation (73–90%; P = 0.776). We detected no effect as a result of the cell sex (P = 0.756). Parent populations were either low in desmin expression (<15% positive cells within the population) or high in desmin expression (>85% positive). (C, bottom) We did not observe any male clone that exhibited a higher RI as compared with the parent population. We transplanted four M-MDSC clonal populations (M1, M2, M3, and M4) and four F-MDSC clonal populations (F1, F2, F3, and F4; mean ± SEM is shown; n = 3 muscle transplantations per clone). In contrast, we found that three of the four F-MDSCs display a high-regenerating potential as observed with their parent population.