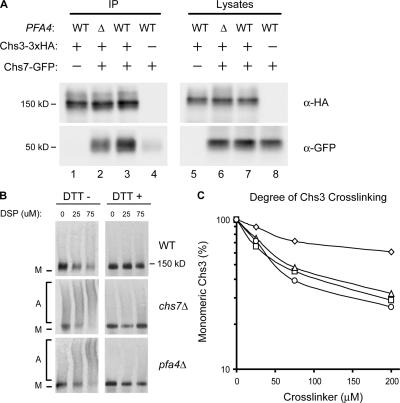
Figure 5.
Loss of PFA4 causes Chs3 aggregation in the ER. (A) Cells expressing Chs3-3xHA and Chs7-GFP were subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-HA antiserum and analyzed by Western blotting with α-HA and α-GFP mAbs. Strains used were KLY46 (lanes 1 and 5), KLY45 + pTM15 (lanes 2 and 6), KLY46 + pTM15 (lanes 3 and 7), and KLY14 + pTM15 (lanes 4 and 8). (B) Lysates of wild-type, chs7Δ, and pfa4Δ cells transformed with plasmid-borne Chs3-3xHA (pHV7) were cross-linked using increasing concentrations of DSP; DTT was added to duplicate samples to reverse cross-links. Chs3 was detected by Western blotting with α-HA mAb. M, monomer; A, aggregates. (C) Cross-linking of chromosomally encoded Chs3-3xHA in wild-type (KLY41; ⋄), chs7Δ (KLY46; ▵), pfa4Δ (KLY43; □), and chs7Δ pfa4Δ (KLY45; ○) strains was performed as for B. Disappearance of monomeric Chs3 as a function of cross-linker concentration was quantified by densitometry.