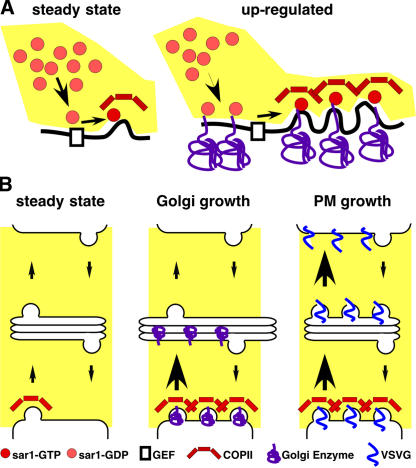
Figure 10.
Model depicting variable exit rate mechanism. (A) COPII assembly is shown at steady state and after up-regulation by increased availability of Golgi residents in the ER membrane. The dibasic signal in the cytoplasmic domain of Golgi residents recruits more Sar1p-GDP to the ER membrane. After nucleotide exchange catalyzed by Sec12p and assembly of the prebudding complex, lateral interactions of the coat components leads to new and larger exit site formation. (B) Golgi input/output pathways are schematized before (steady state) or after either increased Golgi resident expression (Golgi growth) or increased plasma membrane protein expression (PM growth). Golgi residents up-regulate COPII assembly, leading to increased ER exit (denoted by larger arrow) and Golgi growth. Plasma membrane proteins up-regulate both ER exit and Golgi exit, leading to, at most, a transient increase in Golgi size.