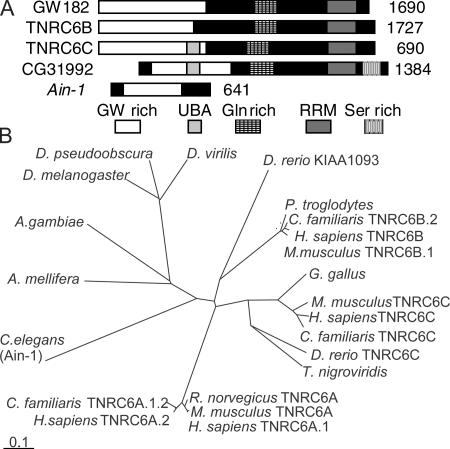
Figure 1.
A comparison of the GW protein family. (A) The product of CG31992, the Drosophila GW protein (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. AE003843), contains three regions that are common to all human GW182-related proteins: an N-terminal GW-rich region, a C-terminal RRM domain, and a glutamine-rich region. It has a predicted ubiquitin-associated domain (UBA) that is also found in TNRC6C and a C-terminal serine-rich region that is not found in human GW proteins. Drosophila GW is 17.8–20% identical and 24–28.3% similar to the human GW protein family. It is most similar to TNRC6C. C. elegans AIN-1 is also suggested to be a member of the GW protein family (Ding et al., 2005) because it is GW rich and contains one region of significant (24%) amino acid similarity. (B) Predicted evolutionary relationships between GW proteins from vertebrates and invertebrates. Bar, 0.1 amino acid substitutions per site.