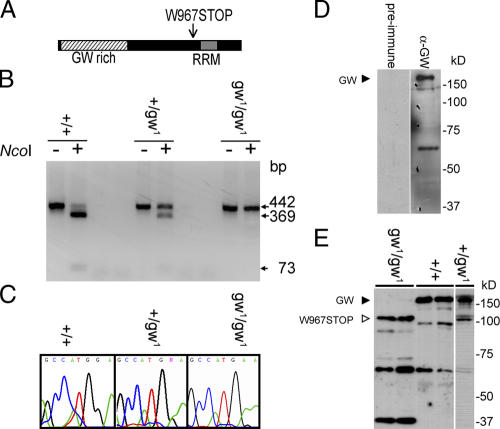
Figure 2.
Characterization of the gw mutation and localization of the GW protein. (A) gw 1 is caused by a nonsense mutation of the tryptophan codon at position 967 to stop. (B) The gw 1 mutation causes the loss of an NcoI restriction site and allowed rapid embryo genotyping by PCR. (C) Mutations were confirmed by DNA sequencing. (D) A polyclonal antibody raised against the N-terminal region of GW recognizes a 160-kD band representing the endogenous protein. (E) The anti-GW antibody also recognizes a 100-kD truncated form of GW in gw1/gw1 embryos that is not present in wild-type embryos.