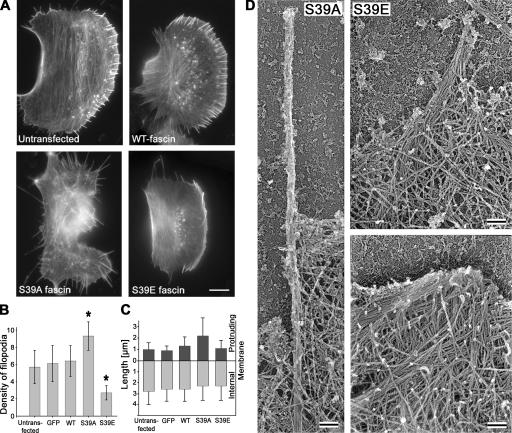
Figure 5.
Effects of fascin mutants on filopodia number and length. (A) Phalloidin staining of untransfected cells and cells expressing indicated GFP-fascins. S39A- or S39E-expressing cells show increased or decreased filopodia formation, respectively. (B) Number of filopodia per 20 μm of cell leading edge in cells transfected with indicated constructs. Asterisks indicate statistically significant changes (P < 0.003) compared with untransfected cells. GFP stands for empty GFP vector. Error bars represent the mean ± the SEM. (C) Lengths of the filopodia protruding beyond leading edge (dark gray bars) and internal (light gray bars) parts of filopodia. Expression of S39A fascin increases the length of the protruding parts of filopodia. (D) EM of filopodia in cells transfected with fascin mutants. A filopodium in S39A-expressing cell (left) is long, thin, straight, and tightly bundled. In S39E-expressing cell (right), a filopodium is loosely bundled (top). Many long filaments converge at the leading edge, forming an abnormally large Λ-precursor (bottom). Bars: (A) 10 μm; (D) 100 nm.