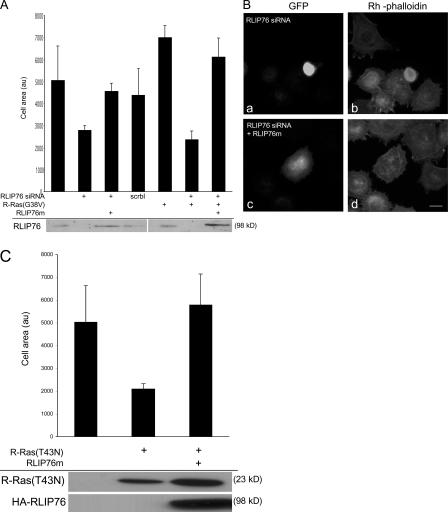
Figure 2.
RLIP76 is required for R-Ras–induced cell spreading. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with R-Ras(G38V) in the presence or absence of 50 pmol of a double-stranded siRNA targeting both human and mouse RLIP76 (RLIP76 siRNA; Rosse et al., 2003) or a sequence-scrambled siRNA (scrbl). Cell lysates were blotted with anti-RLIP76 antibodies. RLIP76 expression was restored in siRNA-transfected cells by coexpression of RLIP76 cDNA containing three silent mutations in the siRNA target site (RLIP76m). Cells were plated on fibronectin-coated coverslips and cell area was measured as described in Materials and methods. Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. (B) Representative micrographs (a and c, GFP to mark transfected cells; b and d, rhodamine-phalloidin to detect F-actin) of cells spreading on fibronectin; cells were transfected with RLIP76 siRNA in the absence (a and b) or presence of the RLIP76m rescue construct (c and d). Bar, 5 μm. (C) NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with dominant-negative R-Ras(T43N), with or without cotransfection with RLIP76, and cell spreading was measured as described in Materials and methods. Mean area measurements of GFP-positive cells are representative of at least three independent experiments and are shown ± the SEM. Expression levels of the transfected proteins were assayed by Western blotting with antibodies to R-Ras (top) or HA (bottom).