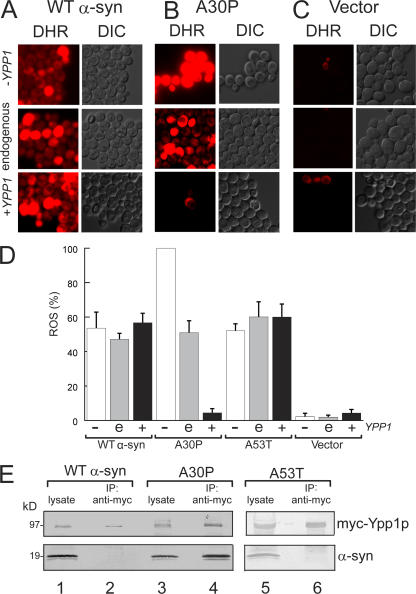
Figure 2.
YPP1 suppresses ROS accumulation in A30P expressing cells. ROS accumulation in cells expressing A30P (pTF302) (A), WT α-syn (pTF301) (B), or vector control cells (pTF300) (C). The “Hughes” YPP1 strain that contains a titratable promoter was used in these experiments. This strain transformed with pTF602 (YPP1) or pTF604 (empty vector) was used for these experiments. For shutting off YPP1 (+doxy), cells were pregrown in noninducing media with 20 μM doxycycline for 7 h, and then shifted into inducing media with doxycycline. For experiments with Ypp1p overexpression, cells were pregrown in noninducing media to mid-log, and then shifted into inducing media. The images shown in all panels were obtained at 3 h in inducing media. The dye DHR123 was added after 2 h in inducing media to give 5 μg/ml, and the cells were then washed before image acquisition. DHR, rhodamine 123. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) Plot of the percentage of cells that exhibited red fluorescence (mean ± SD). The number of cells counted for each group was n = 640 to 1,200. The symbols "−", “e”, and “+” indicate decreased (with doxycycline), endogenous, and increased levels of Ypp1p, respectively. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation shows selective binding of myc-Ypp1p to A30P. Cells expressing the various α-syns and overexpressing myc-tagged Ypp1p were lysed, the extract was incubated with an anti-myc antibody-protein A resin, and the resin was boiled and reduced and subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The top panels show the ∼95-kD band due to myc-Ypp1p; the bottom panels show α-syn. Lane 1, WT α-syn lysate; lane 2, myc-Ypp1p fails to pull down WT α-syn; lane 3, A30P lysate; lane 4, myc-Ypp1p pulls down A30P; lane 5, A53T lysate; lane 6, myc-Ypp1p fails to pull down A53T. The FY23 strain was transformed with pTF201 (WT α-syn), pTF202 (A30P), or pTF203 (A53T) and with pTF504 (myc-YPP1) or pTF503 (empty vector).