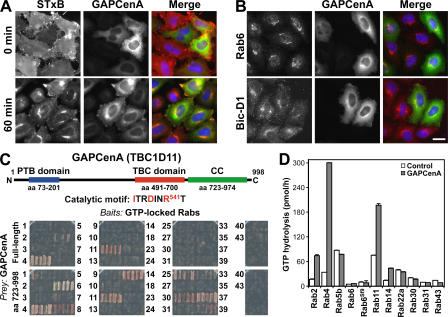
Figure 3.
TBC1D11/GAPCenA is a GAP for Rab4 and does not block Shiga toxin uptake. (A) HeLa cells transfected with GFP-tagged TBC1D11/GAPCenA (green) were used for Shiga toxin uptake assays (red). (B) The ability of Rab6 and Bicaudal-D1 (red) to localize to the Golgi was tested in cells expressing GFP-tagged TBC1D11/GAPCenA (green). (C) A schematic of TBC1D11/GAPCenA shows the putative phosphotyrosine-binding domain (PTB; blue), the TBC domain (red), and a C-terminal coiled-coil region (green). Full-length TBC1D11/GAPCenA and the C-terminal coiled-coil region identified by unbiased yeast two-hybrid library screen prey constructs were tested against the human Rabome bait construct library as described in Materials and methods. All conditions showed equal growth on nonselective media; the ability to grow on the selective media shown in the figure is an indicator of an interaction between the bait and prey. (D) GAP assays were performed using 0.5 pmol of recombinant TBC1D11/GAPCenA (closed bars) or a buffer control (open bars) and 100 pmol of the Rabs indicated in the figure. Two preparations of Rab6 were used: one from bacteria (Rab6), and the other a prenylated preparation produced in insect cells (Rab6Sf9). Error bars represent SD. Bar, 10 μm.