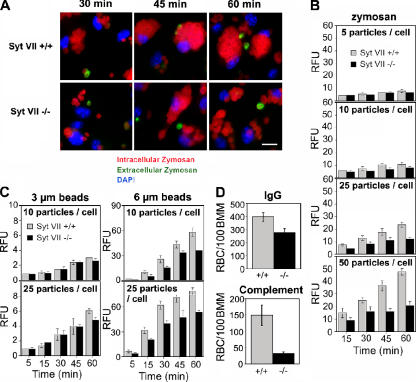
Figure 1.
The phagocytosis defect of Syt VII−/− BMMs increases with particle load and size. (A) Syt VII+/+ or VII−/− BMMs were exposed to 25 IgG-opsonized zymosan red particles/cell for the periods of time indicated. Cells were washed, fixed, and stained without permeabilization to detect extracellular particles (green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue). Bar, 10 μm. (B) The phagocytosis defect of Syt VII−/− BMMs increases with particle load. Opsonized zymosan red uptake was determined fluorometrically at the indicated time points after incubation with increasing numbers of particles/cell. (C) The phagocytosis defect of Syt VII−/− BMMs increases with particle size. The uptake of IgG-opsonized fluorescent polystyrene particles was determined fluorometrically at the indicated time points after incubation with 10 or 25 particles/cell. RFU, relative fluorescence unit. (D) The uptake defect of Syt VII−/− BMMs is independent of the receptor-mediating phagocytosis. The number of internalized sheep RBCs opsonized with IgG or complement was determined after BMM exposure to 10 particles/cell for 30 min. The data represent the mean ± SD (error bars) of triplicates.