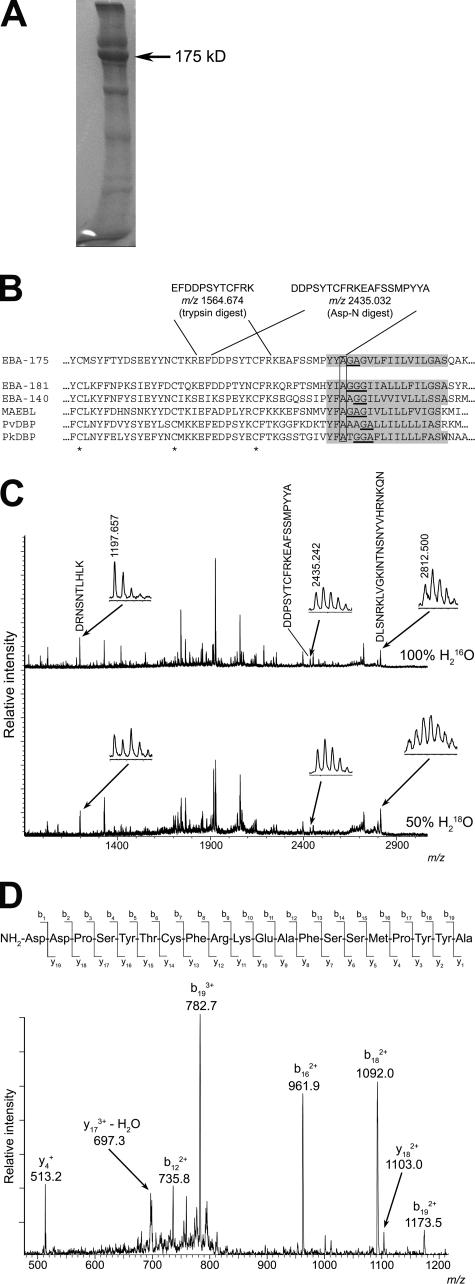
Figure 3.
EBA-175 is shed by intramembrane cleavage. (A) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of partially purified shed EBA-175 (arrow). A total of ∼40 μg of EBA-175 was obtained from 3 liters of culture medium. (B) The most C-terminal intact tryptic and Asp-N peptides identified in digests of EBA-175, with calculated m/z values in carbamidomethylated form, are shown in relation to the juxtamembrane sequence of 3D7 EBA-175 (PlasmoDB ID PF07_0128). The TMD (TMHMM v2.0) is shaded. The sequence is aligned with corresponding sequence from P. falciparum paralogues EBA-181 (PFA0125c) and EBA-140 (MAL13P1.60), as well as P. falciparum MAEBL (PF11_0486), P. vivax DBP (available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession no. P22290), and P. knowlesi DBP (available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession no. P22545). Conserved cysteines are marked with an asterisk. Helix breaking motifs constituting potential rhomboid recognition sites within the TMD are underlined, and the conserved Ala at which EBA-175 is cleaved is boxed. (C) MALDI-TOF spectra of EBA-175 Asp-N digests performed in 100% H2 16O or 50% (vol/vol) H2 18O. The peak matching 1408DDPSYTCFRKEAFSSMPYYA1427 (arrow; shown magnified in inset, with observed m/z value) is not 18O-labeled in the lower spectrum, indicating that it derives from the C terminus. For comparison, peaks corresponding to 1227DRNSNTLHLK1236 (calculated m/z 1197.634) and 562DLSNRKLVGKINTNSNYVHRNKQN585 (calculated m/z 2812.493) are indicated as examples of species that in the lower spectrum exhibit the 18O-labeled isotope pattern typical of internal peptides. (D) Collision-induced fragmentation spectrum of the unlabeled m/z 2435.242 peptide in Asp-N digests. The indicated fragment peaks can be assigned to a b and y series of ions, with the b18 and b19 ions assigning the C-terminal peptide sequence Y-A. The remaining major ions are all consistent with the indicated sequence.