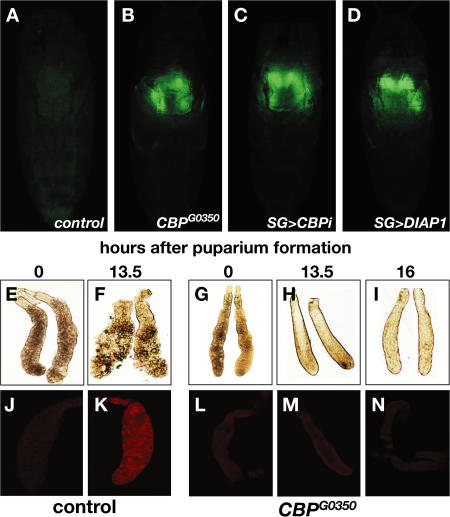
Figure 1.
Mutations in CBP block ecdysone-triggered programmed cell death of larval salivary glands. (A–D) Living animals assayed 24 h APF with a GFP reporter expressed in larval salivary glands. (A) Salivary glands are no longer detectable in control pupae (w; UAS-GFP; SG-GAL4) but persist in CBP mutants (CBPG0350; UAS-GFP/+; SG-GAL4/+) (B) or salivary glands in which CBP is inactivated by RNAi (w; UAS-CBP-RNAi/ UAS-GFP; SG-GAL4/+) (C) or in which diap1 is overexpressed (w; UAS-diap1/UAS-GFP; SG-GAL4/+) (D). (E and F) Larval salivary glands dissected at 0 or 13.5 h APF from controls or 0-, 13.5-, or 16-h CBPG0350 animals (G–I). (J and K) Control and CBPG0350 mutant (L–N) salivary glands stained for the cleaved active form of caspase-3.