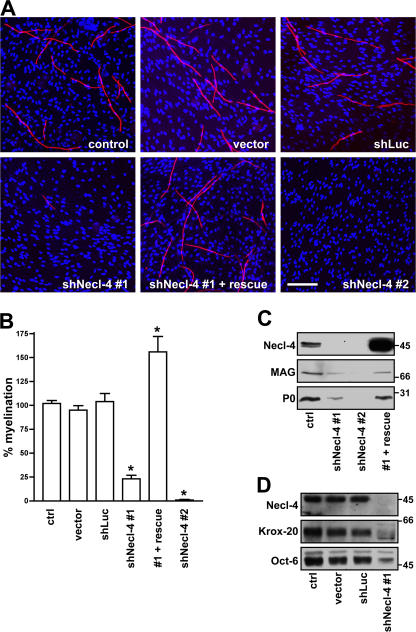
Figure 6.
Necl-4 expression is required for Schwann cell differentiation and myelination. (A) Representative images of myelinating cocultures in which control Schwann cells or Schwann cells infected with the lentiviral vector alone or lentiviruses encoding shRNA to a nonspecific sequence (shLuc) or to Necl-4 sequences, in one case rescued with an exogenous Necl-4 protein (shNecl-4 #1 + rescue), were added to DRG neurons under myelinating conditions. Myelin segments were stained for MBP (red) and with the Hoechst nuclear dye (blue). (B) Quantitation of the effects of Necl-4 knockdowns on Schwann cell myelination. Control Schwann cells or Schwann cells infected with the lentiviral vector alone or viruses encoding shRNAs to luciferase or Necl-4 with or without rescue by an shRNA-resistant Necl-4 were seeded onto dissociated DRG neuron cultures and maintained under myelinating conditions for 10 d. The number of myelin segments that formed were quantitated from three separate experiments (mean ± SEM [error bars]); controls were normalized to 100%. *, P < 0.001. (C) Knockdown of Necl-4 inhibits myelin protein expression. Lysates from control Schwann cells and cells infected with lentiviruses encoding shRNAs to Necl-4, including cells rescued with a modified Necl-4 protein, were blotted for Necl-4 and the myelin proteins MAG and P0; cultures correspond to those shown in Fig. 6 A. shRNA treatment effectively knocked down Necl-4 and myelin protein and was restored by the overexpression of an shRNA-resistant Necl-4. (D) Knockdown of Necl-4 inhibits the expression of myelin transcription factors. Western blot analysis demonstrates the substantial knockdown of Necl-4 and corresponding reductions of the transcription factors Krox-20 and Oct-6. Bar, 100 μm.