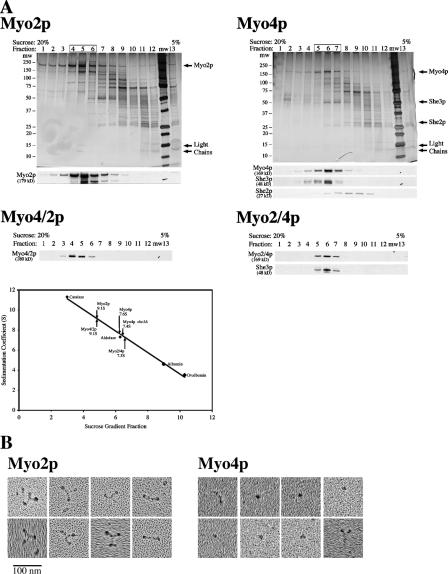
Figure 2.
Hydrodynamic and EM analysis of partially purified myosins. (A) TEV-eluted Myo4p, Myo2p, Myo2/4p, and Myo4/2p were analyzed by velocity sedimentation in 5–20% sucrose gradients. Fractions were collected from the bottom of the gradient and analyzed by silver stain and Western blot. Parallel gradients containing the protein standards catalase, aldolase, albumin, and ovalbumin were used to generate a sedimentation coefficient curve and obtain sedimentation coefficient values of 9.1 ± 0.6S for Myo2p (n = 5), 7.6 ± 0.3S for Myo4p/She3p (n = 8), 7.4 ± 0.2S for Myo4p she3Δ, (n = 4), 9.1 ± 0.4S Myo4/2p (n = 2), and 7.3S for Myo2/4p. Note that She2p disassociates from Myo4p and She3p in the sucrose gradient. (B) EM images indicate that Myo2p is a dimer and Myo4p is a monomer. Partially purified (TEV eluted) Myo2p-GFP and Myo4p-GFP were analyzed by rotary shadowing electron microscopy. Representative images of Myo2p-GFP and Myo4p-GFP are shown. Myo2p-GFP images contain many examples of three globular domains linked into a Y-shaped structure. For Myo4p-GFP, the predominant image is of a single dot, likely the motor domain. In a few examples (left-most images), both the head and neck domains are visible. In very rare instances (bottom right), what might be a Myo4p-GFP dimer is visible.