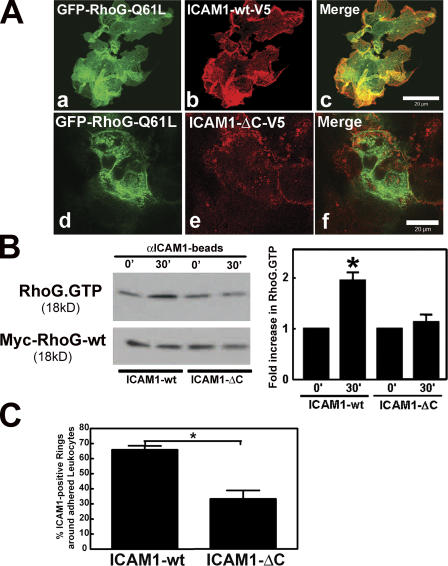
Figure 7.
ICAM1 intracellular domain was required for RhoG localization and activation. (A) COS7 cells were transiently cotransfected with full-length ICAM1 tagged with V5 (b) or a C-terminal deletion mutant of ICAM1-V5 (ICAM1-ΔC-V5; e) and with GFP–RhoG-Q61L (a and d). Panels c and f show the corresponding merged images. ICAM1-ΔC-V5 does not colocalize with RhoG-Q61L. (B) Experiments were performed as described in Fig. 6 C except ICAM1-GFP has been replaced with V5-tagged ICAM1-wt (ICAM1-wt) or the V5-tagged C-terminal truncated ICAM1 mutant (ICAM1-ΔC). The top panel shows that ICAM1 engagement increases RhoG-GTP levels in cells expressing ICAM1-wt but not in cells expressing ICAM1-ΔC. The bottom panel shows levels of myc-RhoG-wt in total cell lysates. The graph on the right shows quantification of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (C) ICAM1 intracellular tail was required for efficient recruitment around an adhered leukocyte. Confocal imaging was used to visualize the apical and the baso- lateral plane of the COS7 cells that were expressing either ICAM1-wt or ICAM1-ΔC. Quantification of ICAM1-rich rings around HL60 cells that were allowed to adhere for 30 min showed a requirement of the ICAM1 tail for proper cup formation. The experiment was repeated three times. *, P < 0.01. (B and C) Data are means ± SEM (error bars). Bars, 20 μm.