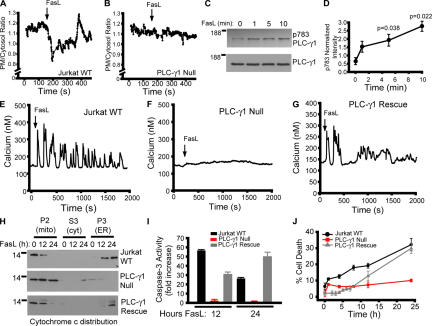
Figure 1.
Requirement of PLC-δ1 for FasL-mediated apoptosis in Jurkat cells. (A) Plasma membrane (PM) to cytosol translocation of the phosphoinositide 4,5-bisphophate biosensor PLCδ-PH-GFP in wild-type Jurkat cells. (B) Jurkat cells lacking PLC-γ1 expression (Irvin et al., 2000). (C) PLC-γ1 activation indicated by phosphotyrosine 783 immunoblotting (p783 PLC-γ1) and total PLC-γ1 as a function of time. (D) Quantification of PLC-γ1 phosphorylation normalized to control. (E) Calcium response of Jurkat cells treated with 10 ng/ml FasL. Shown is a single-cell response representative of multiple determinations. Single-cell calcium responses of PLC-γ1–null (F) and PLC-γ1–rescued cells (G). (H) Cytochrome c release from mitochondria and translocation to the ER in response to FasL stimulation for 0, 12, or 24 h in WT, PLC-γ1–null, or PLC-γ1–rescued cells. Mito/P2, mitochondrial-enriched fraction; cyt/S3, cytosol fraction; ER/P3, ER-enriched fraction. (I) Caspase-3 activity in WT, PLC-γ1–null, and PLC-γ1–rescued cells. (J) Cell death (propidium iodide–positive cells as a percentage of the total) in WT, PLC-γ1–null, and PLC-γ1–rescued cells. Data is presented as the mean ± the SEM.