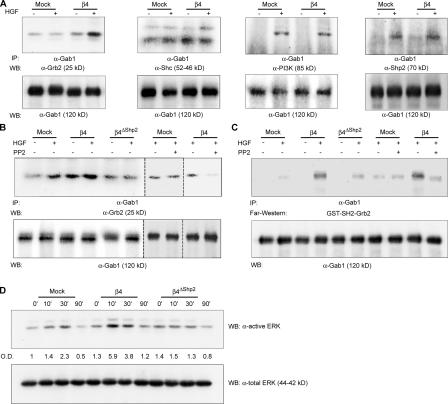
Figure 3.
β4-dependent activation of Src leads to the selective association of Gab1 with Grb2 and to the increased activation of ERK/MAPKs. (A) HGF stimulation results in the increased association of Gab1 with Grb2 in β4 cells. MDA-MB-435 mock and β4 cells were transiently transfected with Gab1 and stimulated with 100 ng/ml HGF for 30 min. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to Gab1, and blots were probed as indicated. Densitometric analysis of the blots obtained in four experiments indicates that the HGF-dependent association of Grb2 with Gab1 in mock cells is increased 1.26-fold (± 0.48) compared with nonstimulated cells, whereas the HGF-dependent association of Gab1 with Grb2 in β4 cells is increased 4.7-fold (± 0.98; P < 0.01). (B) Abrogation of Shp2 binding or Src inhibition with PP2 impairs the coimmunoprecipitation of Gab1 with Grb2 in β4 cells. Dotted lines indicate the grouping of images from different parts of the same gel. (C) Far-Western analysis showing the association between immunoprecipitated Gab1 and GST-SH2-Grb2. In accordance with the coimmunoprecipitation data, HGF-dependent Gab1–Grb2 interaction is increased in β4 cells compared with mock and β4ΔShp2 transfectants. PP2-mediated inhibition of Src results in decreased Gab1–Grb2 interaction in β4 but not in mock cells. (D) HGF activates ERK/MAPKs longer and more efficiently in β4 cells than in mock or β4ΔShp2 cells. Cells were treated with 100 ng/ml HGF for the indicated times, and total lysates were probed on blots as indicated. Band intensities were quantitated by densitometric analysis with respect to total protein content.