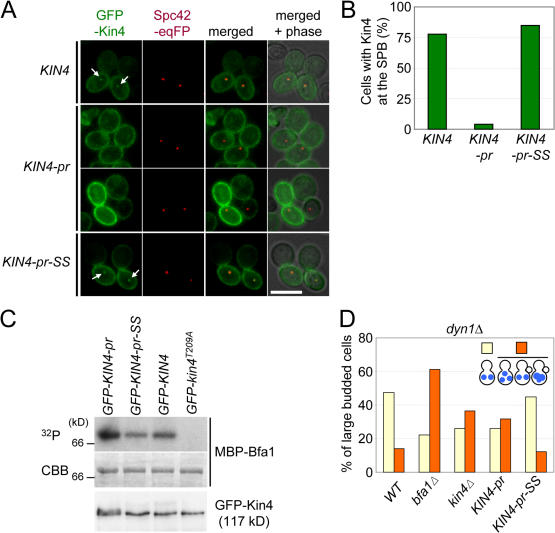
Figure 5.
Plasma membrane–bound Kin4 fails to promote SPOC function. (A) Localization of GFP-Kin4, GFP–Kin4-pr, and GFP–Kin4-pr-SS. The indicated cells carrying SPC42-eqFP611 were grown in YPR medium. After 2 h of incubation with nocodazole, galactose was added for 1 h to induce the expression of the pGal1-GFP-KIN4 constructs. Cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. The arrows point toward SPB-associated Kin4-GFP signals. (B) Quantification of A. n > 50 large-budded cells per strain. (C) GFP–Kin4-pr, GFP–Kin4-pr-SS, GFP-Kin4, and GFP-Kin4T209A were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies. Kin4 kinase activity was determined using purified MBP-Bfa1 as a substrate. A C-terminal degradation product of Bfa1 is shown. The bottom panel shows the GFP-Kin4 levels determined by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibodies. (D) KIN4 and KIN4-pr-SS cells are checkpoint proficient, whereas kin4Δ and KIN4-pr cells are SPOC deficient. The indicated cell types carrying dyn1Δ were incubated at 14°C. DNA was stained with DAPI. The indicated cell types were determined for >100 large-budded cells per strain. Bar, 5 μm.