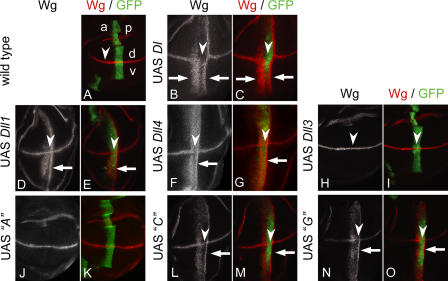
Figure 4.
Activity of Dll1 and Dll3 in D. melanogaster wing discs. Expression of D. melanogaster Dl and vertebrate orthologues with ptcGal4 in the wing imaginal discs. (A) Expression of Wg and ptcGal4 in a wing imaginal disc of the late third larval instar. Wg (red) is induced along the dorsoventral (d-v) compartment boundary by Notch signaling. Expression of UAS GFP (green) reveals the stripe-like expression domain of ptcGal4, which runs perpendicular to the Wg domain at the anterior side of the A-P compartment border. Expression within the ptcGal4 domain increases toward the posterior (right). (B and C) Ectopic Wg activation along the A-P boundary (arrows) induced by ectopic expression of D. melanogaster Dl. Two ectopic stripes of Wg expression are induced (arrows). The broader, anterior-located stripe is in the region of low Dl expression. The second thinner is induced in cells adjacent to the ptc domain. In the region with highest expression of Dl, expression of Wg is not induced because of the cis-inhibitory effect of Dl at high levels of expression. Note that high levels of Dl also suppress Notch activity at the dorsoventral boundary as indicated by down-regulation of Wg (arrowheads). Expression of Dll1flag (D and E) or Dll4flag (F and G) along the A-P boundary activates ectopic expression of Wg (arrows) in a pattern similar to Dl. However, the cis-inhibitory effect is weaker than in the case of Dl. (H and I) Expression of Dll3flag has no effect on the activity of the Notch pathway in D. melanogaster. In addition, endogenous expression of Wg along the dorsoventral border is not affected (arrowheads). (J and K) Expression of construct A (Dll1/Dll3 chimera; Fig. 5) does not activate the Notch pathway in D. melanogaster. (L and M) Ectopic Wg activation along the A-P wing border (arrow) by ectopic expression of construct C (Dll1/Dll3 chimera; Fig. 5). In the regions with highest expression, construct C slightly suppresses Notch activity, as indicated by the slight down-regulation of Wg in its normal expression domain (arrowheads). (N and O) Ectopic Wg activation along the A-P wing border (arrows) by ectopic expression of construct G (Dll1/Dll3 chimera; Fig. 5). In the regions with highest expression, construct G slightly suppresses Notch activity, as indicated by the slight down-regulation of Wg in its normal expression domain (arrowheads). Note that construct C, as well as construct G, signals to cells adjacent to the posterior domain boundary (L–O, arrows).