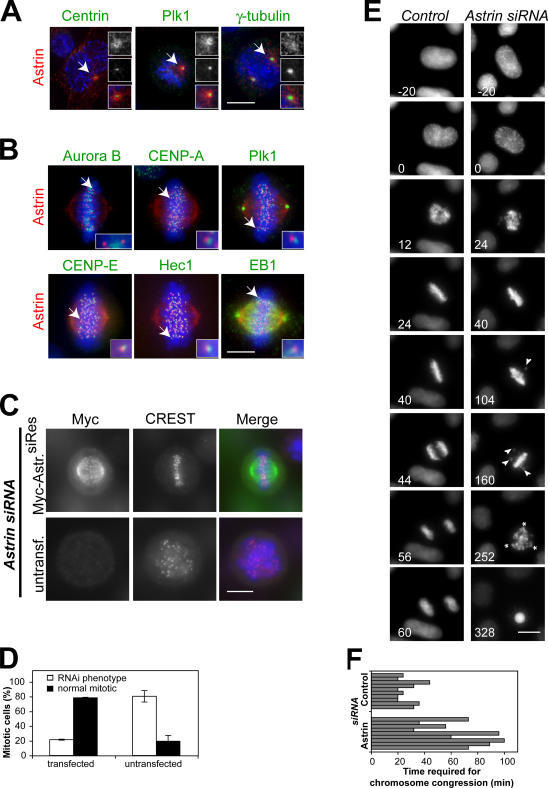
Figure 1.
Astrin depletion results in impaired chromosome alignment and the formation of multipolar spindles. (A) Pro- and prometaphase HeLa cells were stained with antibodies against astrin and centrin, Plk1, or γ-tubulin. Centrosomes indicated with arrows are shown enlarged in the insets. (B) Metaphase HeLa cells were processed for immunofluorescence using antibodies against astrin and aurora B, CENP-A, Plk1, CENP-E, Hec1, or EB1. The kinetochores indicated with arrows are shown enlarged in the insets. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with myc-astrin constructs containing five silent mutations in the sequence targeted by the astrin siRNA oligonucleotide 24 h before transfection with astrin siRNA oligonucleotides and stained with CREST antiserum and antibodies against myc. (D) The percentage of transfected and untransfected cells displaying the astrin depletion phenotype was scored in two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. (E) Stills of representative videos of control and astrin-depleted cells. Time is indicated in minutes. All astrin-depleted cells analyzed (n = 10) exhibited delayed chromosome congression (compare t = 24 min in control and astrin siRNA cells) and unstable metaphase plates. Note the unaligned chromosomes in astrin siRNA at t = 104 min and t = 160 min (arrowheads). The depicted astrin-depleted cell is initially bipolar but forms a multipolar spindle (asterisks indicate spindle poles) during the mitotic arrest. (F) Control or astrin-depleted HeLa S3 cells expressing histone-H2B-GFP were followed by live cell analysis. The time required for chromosome congression was plotted. Bars, 10 μm.