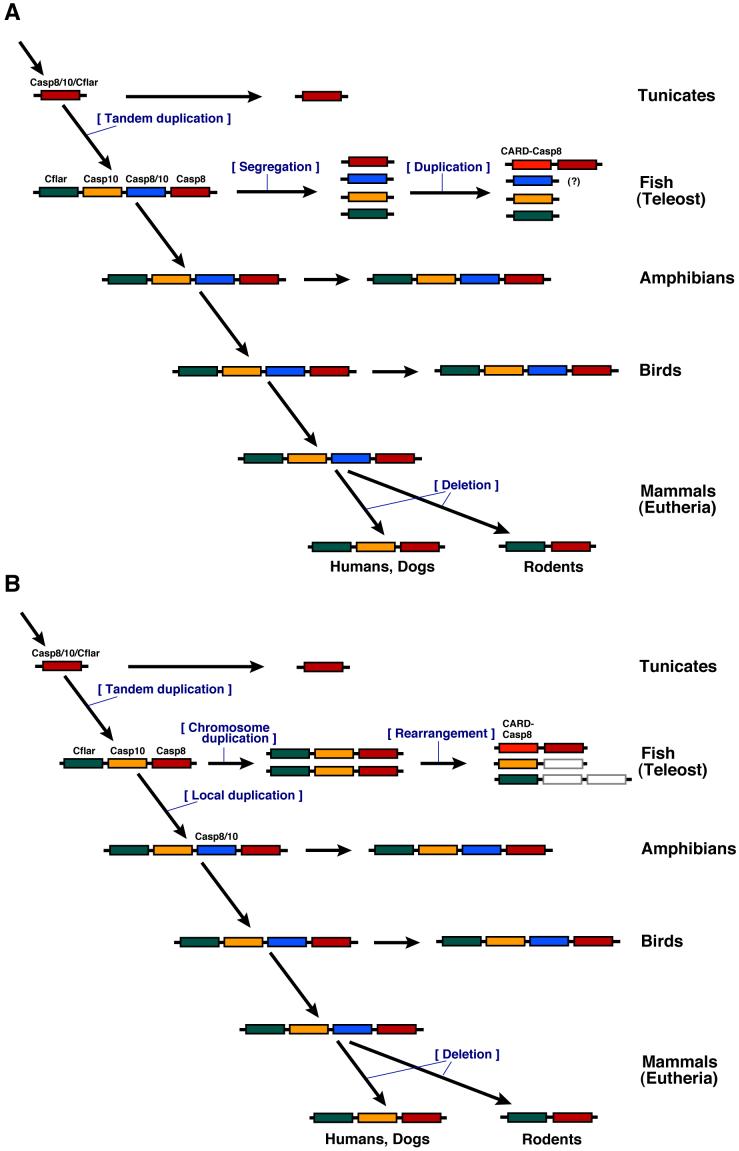
Fig.4.
Summary of the evolutionary insights regarding casp8 and related genes provided by phylogenetic and chromosome mapping analyses.
(Explanation A) Early during vertebrate evolution, the four casp8, casp10, casp8/10 and cflar genes arose from tandem duplication events of the ancestral casp8/10/cflar gene. In the fish lineage, the duplicated genes were further translocated to different chromosomes and the ancient casp8 gene is locally duplicated to become both casp8 and card-casp8. In mammals, the casp10 or a third casp8/10 gene was deleted from the genome. The casp8/10 gene has not yet been identified in the fish. (Explanation B) Early during vertebrate evolution, the three casp8, casp10 and cflar genes arose from tandem duplication of the ancestral casp8/10/cflar gene. In fish, these genes became doubled on chromosomes duplicated by the teleost genome duplication event. During the course of evolution, casp8 but not casp10 was lost from one chromosome, and casp10 but not casp8 was lost from the duplicated chromosome. A chromosome rearrangement also led to separation of the cflar gene from the other genes and a local duplication event generated the casp8 and card-casp8 genes. After evolution to tetrapods, an additional casp8/10 gene arose from duplication and the casp10 or a third casp8/10 gene was deleted from the genome in mammals.