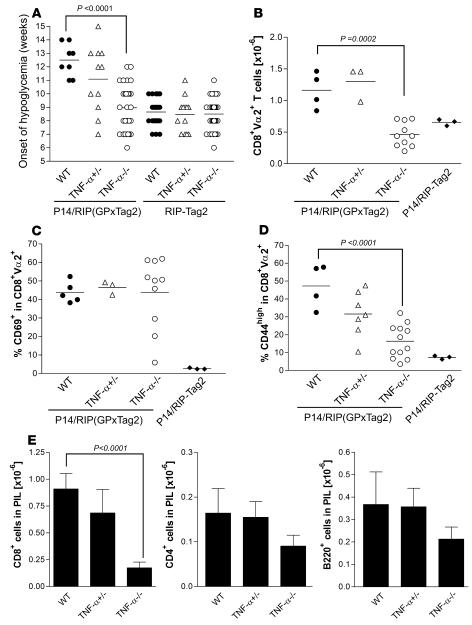
Figure 6. Reduced T cell expansion and tumor infiltration in P14/RIP(GP × Tag2)/TNF-α–/– animals.
(A) Impaired immune surveillance in TNF-α–/– P14/RIP(GP × Tag2) animals. The age at onset of hypoglycemia was determined by weekly measurement of blood glucose levels in mice of the indicated genotype. This was used as a surrogate marker of tumor development and immune surveillance, since it is a direct measure of β islet cell mass. Results obtained for individual mice are shown. Differences between WT and TNF-α–/– P14/RIP(GP × Tag2) animals were statistically significant (P < 0.0001). (B) The number of CD8+Vα2+ P14 cells in PDLN of P14/RIP(GP × Tag2) animals of the indicated genotypes was calculated after flow cytometry analysis of PDLN. Averages and data obtained from individual mice are shown. Differences between WT and TNF-α–/– animals were statistically significant (P = 0.0002). (C and D) The proportion of GP-specific P14 CD8+ T cells expressing high levels of the activation markers CD69 (C) and CD44 (D) was assessed in PDLN after gating on CD8+Vα2+ cells. Averages and data obtained from individual mice are shown. iLN data are also shown as a control. Differences between WT and TNF-α–/– animals were statistically significant for CD44 (P < 0.0001). (E) Pancreas-infiltrating leukocytes (PIL) were isolated from P14/RIP(GP × Tag2) WT, TNF-α+/–, or TNF-α–/– pancreas, and the number of infiltrating CD8+, CD4+, and B220+ cells was determined by flow cytometry and analysis of the leukocytic infiltrates. Error bars indicate SEM. The number of CD8+ cells in PILs from P14/RIP(GP × Tag2)/TNF-α–/– mice was significantly lower than in those from P14 WT/RIP(GP × Tag2) animals (P < 0.0001) (WT mice: n = 5; TNF-α–/– mice: n = 10).