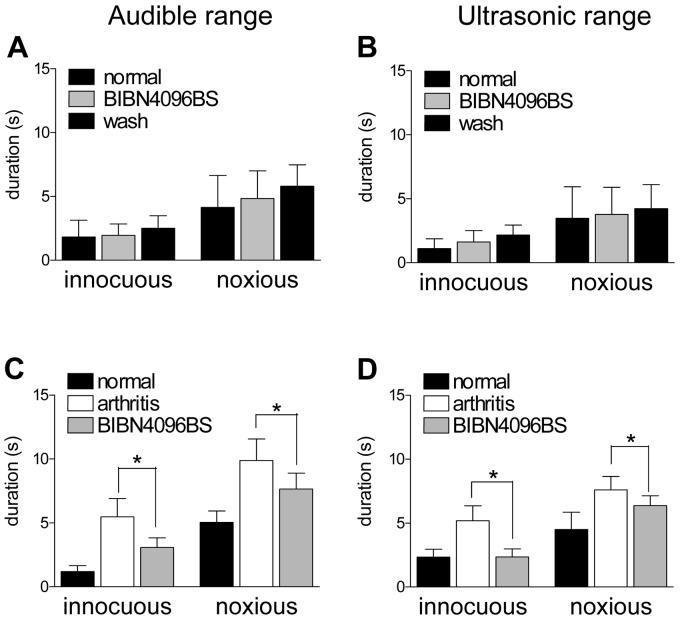
Figure 7. Spinal administration of BIBN4096BS inhibits increased vocalizations of arthritic animals.
(A) and (B) In normal animals, BIBN4096BS (1 μM; 15 min) had no effect on the vocalizations in the audible (A, C) and ultrasonic (B, D) ranges evoked by innocuous (500 g/30 mm2) and noxious (2000 g/30 mm2) stimulation of the knee (n = 3). (C) and (D) BIBN4096BS (1 μM; 15 min) significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the vocalizations of arthritic animals (n = 8). In this group of animals, vocalizations were recorded before (normal) and 5-6 h after arthritis induction (arthritis) and during intrathecal application of BIBN4096BS (1 μM; 15 min). * P < 0.05 (paired t-test).