Abstract
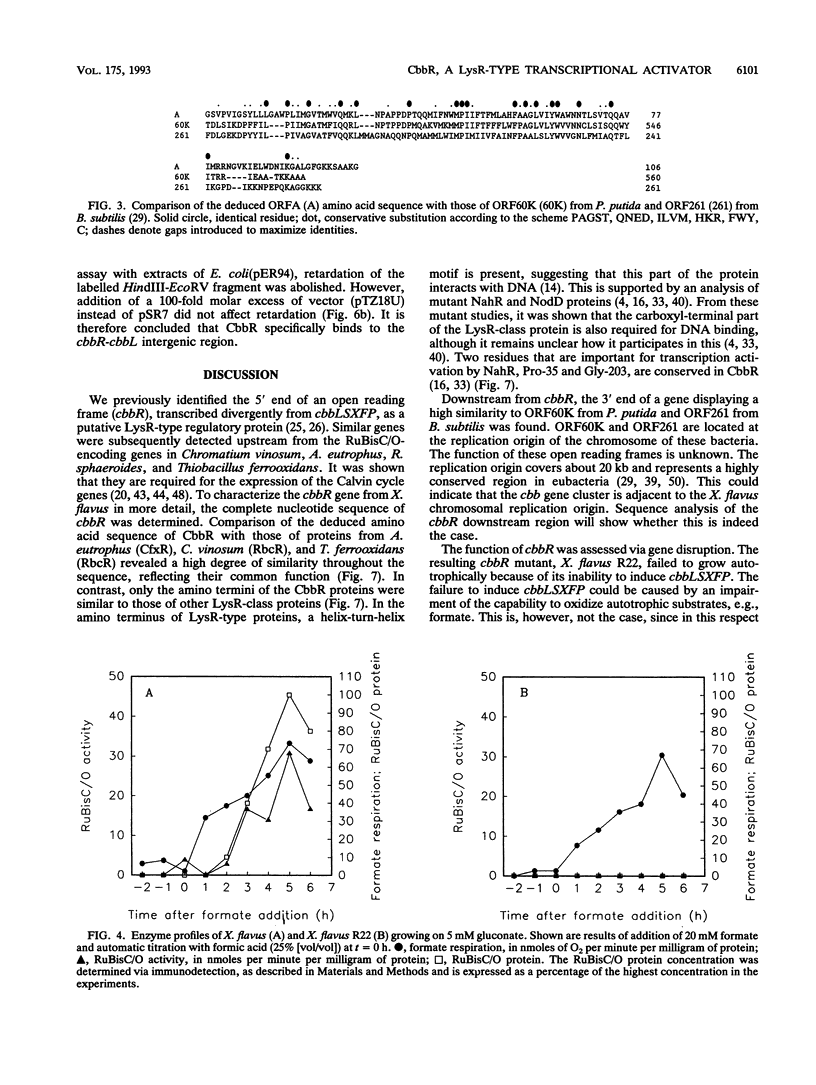
Xanthobacter flavus is able to grow autotrophically with the enzymes of the Calvin cycle for the fixation of CO2, which are specified by the cbbLSXFP gene cluster. Previously, the 5' end of an open reading frame (cbbR), displaying a high sequence similarity to the LysR family of regulatory proteins and transcribed divergently from cbbLSXFP, was identified (W. G. Meijer, A. C. Arnberg, H. G. Enequist, P. Terpstra, M. E. Lidstrom, and L. Dijkhuizen, Mol. Gen. Genet. 225:320-330, 1991). This paper reports the complete nucleotide sequence of cbbR and a functional characterization of the gene. The cbbR gene of X. flavus specifies a 333-amino-acid polypeptide, with a molecular weight of 35,971. Downstream from cbbR, the 3' end of an open reading frame displaying a high similarity to ORF60K from Pseudomonas putida and ORF261 from Bacillus subtilis was identified. ORF60K and ORF261 are located at the replication origin of the bacterial chromosome. Inactivation of cbbR, via the insertion of an antibiotic resistance gene, rendered X. flavus unable to grow autotrophically. This was caused not by an inability to oxidize autotrophic substrates (e.g., formate) but by a complete lack of expression of the cbb genes. The expression of the CbbR protein in Escherichia coli was achieved by placing cbbR behind a strong promoter and optimization of the translational signals of cbbR. CbbR binds specifically to two binding sites in the cbbR-cbbL intergenic region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. E., Hamilton W. D., Wootton J. C., Johnston A. W. Single and multiple mutations affecting properties of the regulatory gene nodD of Rhizobium. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1567–1577. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Crawford I. P. The roles of indoleglycerol phosphate and the TrpI protein in the expression of trpBA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):979–988. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkhuizen L., Harder W. Substrate inhibition in Pseudomonas oxalaticus OX1: a kinetic study of growth inhibition by oxalate and formate using extended cultures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1975;41(2):135–146. doi: 10.1007/BF02565045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Gussin G. N. Mutations in TrpI binding site II that differentially affect activation of the trpBA promoter of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4137–4144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goethals K., Van Montagu M., Holsters M. Conserved motifs in a divergent nod box of Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 reveal a common structure in promoters regulated by LysR-type proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusterspreute M., Ha Thi V., Emery S., Tournis-Gamble S., Kennedy N., Davison J. Vectors with restriction site banks. IV. pJRD184, a 3793-bp plasmid vector with 49 unique restriction sites. Gene. 1985;39(2-3):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. Z., Schell M. A. In vivo interactions of the NahR transcriptional activator with its target sequences. Inducer-mediated changes resulting in transcription activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10830–10838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouanneau Y., Tabita F. R. Independent regulation of synthesis of form I and form II ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):620–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.620-624.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khudyakov YuE, Neplyueva V. S., Kalinina T. I., Smirnov V. D. Effect of structure of the initiator codon on translation in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):369–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano T., Sugawara K. Specific binding of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans RbcR to the intergenic sequence between the rbc operon and the rbcR gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):1019–1025. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.1019-1025.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmicke L. G., Lidstrom M. E. Organization of genes necessary for growth of the hydrogen-methanol autotroph Xanthobacter sp. strain H4-14 on hydrogen and carbon dioxide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1244–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1244-1249.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levering P. R., van Dijken J. P., Veenhius M., Harder W. Arthrobacter P1, a fast growing versatile methylotroph with amine oxidase as a key enzyme in the metabolism of methylated amines. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Mar;129(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00417184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer W. G., Arnberg A. C., Enequist H. G., Terpstra P., Lidstrom M. E., Dijkhuizen L. Identification and organization of carbon dioxide fixation genes in Xanthobacter flavus H4-14. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):320–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00269865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer W. G., Croes L. M., Jenni B., Lehmicke L. G., Lidstrom M. E., Dijkhuizen L. Characterization of Xanthobacter strains H4-14 and 25a and enzyme profiles after growth under autotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(4):360–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00249006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer W. G., Enequist H. G., Terpstra P., Dijkhuizen L. Nucleotide sequences of the genes encoding fructosebisphosphatase and phosphoribulokinase from Xanthobacter flavus H4-14. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2225–2230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Genes and their organization in the replication origin region of the bacterial chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsek M. R., Shinabarger D. L., Rothmel R. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Roles of CatR and cis,cis-muconate in activation of the catBC operon, which is involved in benzoate degradation in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7798–7806. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7798-7806.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothmel R. K., Shinabarger D. L., Parsek M. R., Aldrich T. L., Chakrabarty A. M. Functional analysis of the Pseudomonas putida regulatory protein CatR: transcriptional studies and determination of the CatR DNA-binding site by hydroxyl-radical footprinting. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4717–4724. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4717-4724.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Brown P. H., Raju S. Use of saturation mutagenesis to localize probable functional domains in the NahR protein, a LysR-type transcription activator. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3844–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Poser E. F. Demonstration, characterization, and mutational analysis of NahR protein binding to nah and sal promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):837–846. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.837-846.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Sukordhaman M. Evidence that the transcription activator encoded by the Pseudomonas putida nahR gene is evolutionarily related to the transcription activators encoded by the Rhizobium nodD genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1952–1959. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1952-1959.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Regulation of nodulation gene expression by NodD in rhizobia. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5177–5182. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5177-5182.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Yee T. W., Baird C., Krishnapillai V. Pseudomonad replication origins: a paradigm for bacterial origins? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2581–2587. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Gibson J. L., Bowien B., Dijkhuizen L., Meijer W. G. Uniform designation for genes of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham reductive pentose phosphate pathway of bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):107–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R. Molecular and cellular regulation of autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation in microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):155–189. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.155-189.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viale A. M., Kobayashi H., Akazawa T., Henikoff S. rbcR [correction of rcbR], a gene coding for a member of the LysR family of transcriptional regulators, is located upstream of the expressed set of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase genes in the photosynthetic bacterium Chromatium vinosum. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5224–5229. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5224-5229.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hatfield G. W. Transcriptional activation at adjacent operators in the divergent-overlapping ilvY and ilvC promoters of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):643–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhövel U., Bowien B. Identification of cfxR, an activator gene of autotrophic CO2 fixation in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2695–2705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ogasawara N. Structure and function of DnaA and the DnaA-box in eubacteria: evolutionary relationships of bacterial replication origins. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2589–2597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]