Figure 1.
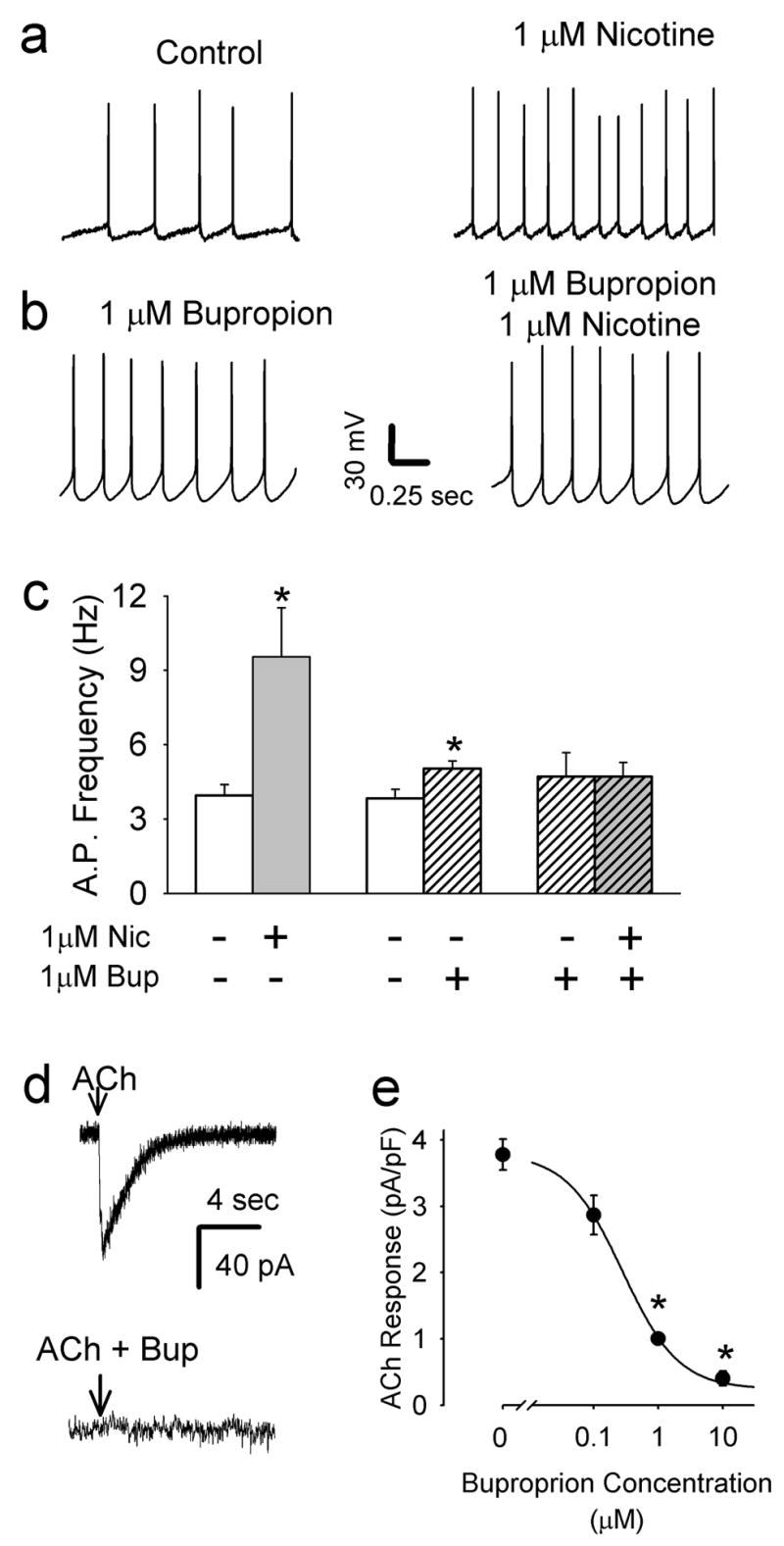
Bupropion inhibits nAChRs on VTA dopamine neurons. a) Bath application of 1 μM nicotine increases action potential frequency (n = 7). b) In slices pretreated with 1 μM bupropion nicotine does not alter action potential frequency in dopamine neurons (n = 4). c) Summary of average action potential firing rates in VTA dopamine neurons under different treatement paradigms. Acute application of nicotine (1μM) induced a significant increase in action potential activity relative to pre-nicotine baseline activity (n = 7, * p<0.05 by paired t-test). In acute tests of bupropion’s effects on action potential activity, baseline firing rate was sampled and averaged over 2 min immediately prior to 1 μM bupropion, which was perfused for at least 20 min prior to sampling the frequency for another 2 min. Under these conditions, bupropion also a significant increase in firing rate (n=6, * p<0.05 by paired t-test), but the magnitude of the change was smaller than nicotine. d) For assessing interaction of bupropion with nAChRs directly, responses to focal application of 1 mM ACh onto VTA dopamine neurons were used. In control cells without bupropion treatment, rapid inward currents were seen in the presence of inhibitors of synaptic transmission. The lower trace illustrates the lack of response from a neuron following pretreatment with 10 μM bupropion for > 2 hrs. e) To assess the sensitivity to bupropion, slices were pretreated with with various concentrations of the drug for > 2 hrs. Summary data of the inhibition of the ACh-induced inward current by a range of bupropion concentrations. (N= 23, 22, 17, 13 for 0, 0.1, 1, and 10 μM, respectively, * p < 0.01). Note that bupropion also blocks the increase in noise induced by nicotine, as with other nAChR antagonists [20], further supporting the idea that bupropion directly inhibits nAChRs on the dopamine neurons. Recordings of membrane potential were made in amphotericin perforated-patch whole-cell current clamp mode. Recordings of the current induced by nicotine were made in normal whole-cell voltage clamp.
