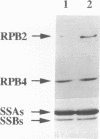
Abstract
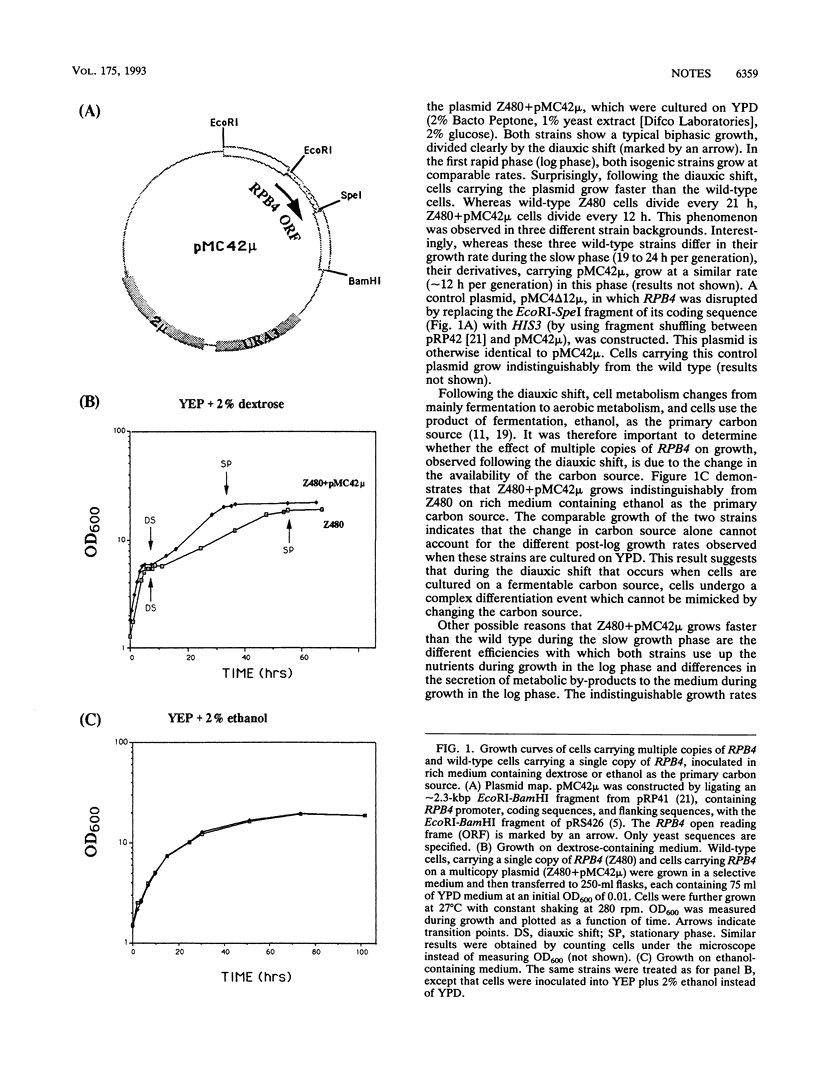
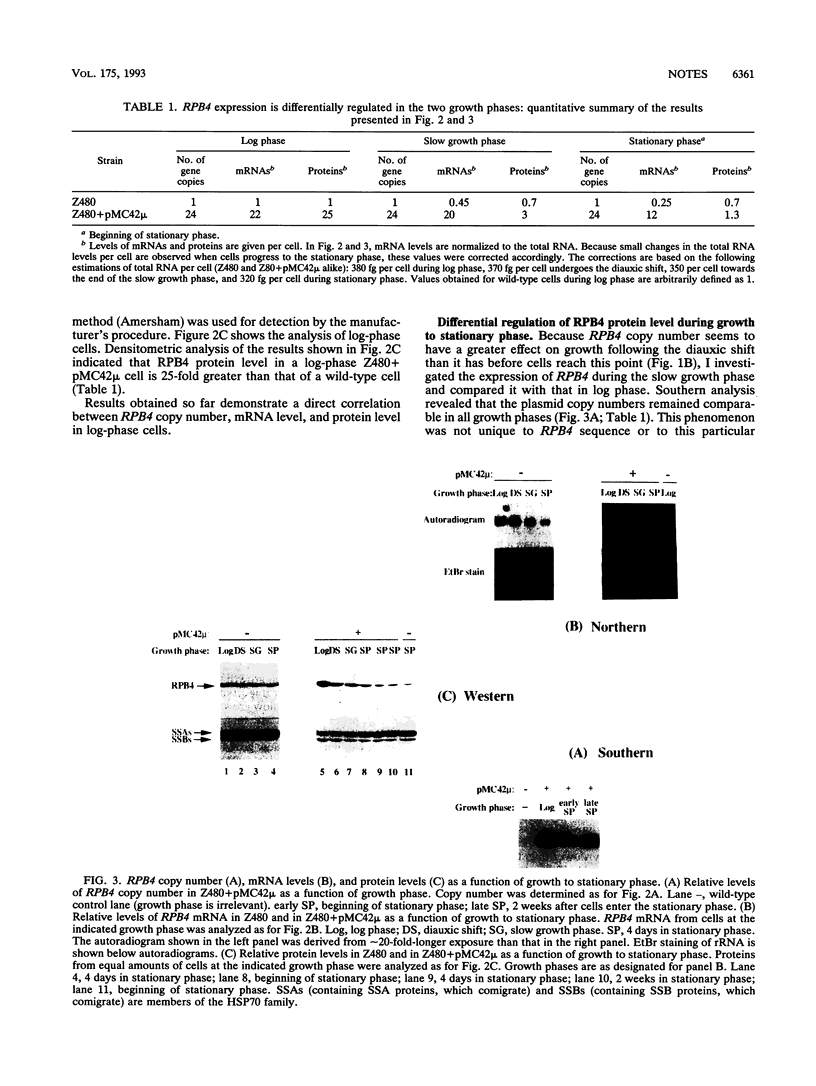
Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, grown on a fermentable carbon source, display two growth phases before they enter the stationary phase: a rapid phase (log phase) followed by a slow phase. It was previously shown that a subunit of the yeast RNA polymerase II, RPB4, positively affects the activity of the enzyme in post-log phases but has little or no effect on its activity in log phase. Here, I show that RPB4 level limits the growth rate during the slow growth phase. Thus, a small increase in RPB4 protein level, in cells carrying multiple copies of the RPB4 gene, results in an almost twofold increase in the growth rate during this phase. Furthermore, RPB4 expression is differentially regulated in the two growth phases. During the slow growth phase, a posttranscriptional process which controls the RPB4 level and thus can control growth rate becomes active. These results reveal a complex growth control mechanism, in which the transcriptional apparatus is probably a limiting element, operating in the last stages of the yeast growth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bataillé N., Régnacq M., Boucherie H. Induction of a heat-shock-type response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae following glucose limitation. Yeast. 1991 May-Jun;7(4):367–378. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorstein W. R., Craig E. A. Regulation of a yeast HSP70 gene by a cAMP responsive transcriptional control element. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2543–2553. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucherie H. Protein synthesis during transition and stationary phases under glucose limitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.385-392.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choder M. A general topoisomerase I-dependent transcriptional repression in the stationary phase in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2315–2326. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Epitope tagging and protein surveillance. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:508–519. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94038-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Mutations in the three largest subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II that affect enzyme assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4669–4678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käppeli O. Regulation of carbon metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and related yeasts. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;28:181–209. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle C. M., Aynardi M. W., Kolodny M. R., Park F. J., Jones E. W. Protease B of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and regulation of the PRB1 structural gene. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):255–263. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praekelt U. M., Meacock P. A. HSP12, a new small heat shock gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of structure, regulation and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00315801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Becker J., Kosic-Smithers J., Craig E. A. Yeast Hsp70 RNA levels vary in response to the physiological status of the cell. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2680–2688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2680-2688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Braun E., Johnston G. C., Singer R. A. Stationary phase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):383–401. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.383-401.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Brown D., Braun E. Bcy1, the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in yeast, is differentially modified in response to the physiological status of the cell. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19704–19709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB4 is essential for high- and low-temperature yeast cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2854–2859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]