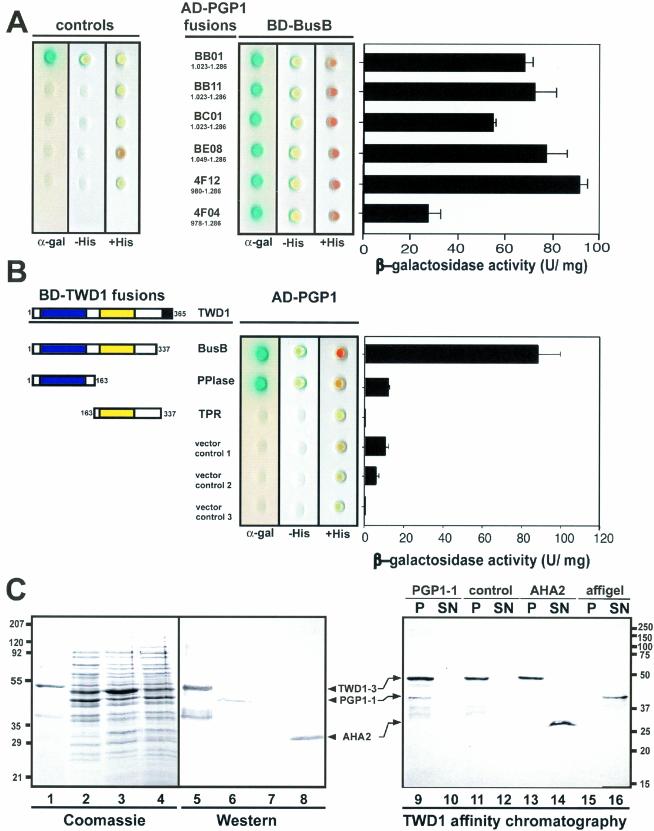
Figure 2.
Analysis of TWD1-AtPGP1 interaction. (A) Interaction between TWD1 (BD-BusB) and six AtPGP1 clones fused to the GAL4 activation domain (AD) isolated in a yeast two-hybrid screen. Controls are from top to bottom: pGBT9.BS-CBL1/pGAD-CIPK (positive control), pGBT9.BS vector/pGAD vector, BD-BusB/AD vector, BD vector/AD-4F12, and AD vector/BD vector (negative controls). (B) The PPIase-like domain of TWD1 is responsible for the interaction with AtPGP1. The PPIase-like and the TPR-domain of TWD1 as GAL4 binding domain (BD) fusions were tested against activation domain AD-PGP1 fusion (clone 4F12). Colored boxes represent the following putative functional domains: blue, cis-trans-peptidyl proly isomerase domain; yellow, tetratrico-peptide repeat; black, membrane anchor. Transformants were analyzed for histidine auxotrophy and LacZ (β-galactosidase) reporter activity. Single colonies were spotted on selective media plates supplemented with X-α-Gal. LacZ reporter activities were quantified by liquid culture assays and are displayed as units per mg protein; error bars represent SDs from three to five independent transformants. (C) Ni-affinity–purified TWD1–3 (lane 1 and 5) and cleared total E. coli lysates containing the expressed C-termini of AtPGP1 (lane 2 and 6), the vector control (lane 3 and 7) and the C-terminus of Arabidopsis H+-ATPase AHA2 (lane 4 and 8) were visualized as Coomassie Blue stain (left panel) and immunoprobed (middle panel) as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. A TWD1 affinity matrix was incubated with cleared E. coli lysates containing the expressed C-termini of AtPGP1, the vector control or the C-terminus of Arabidopsis H+-ATPase AHA2. As negative control, empty affigel beads were incubated with the AtPGP1-1 lysate. Equal volumes of matrix-eluted (P) as well as unbound proteins (SN) were separated by PAGE, and immunoprobed using the antisera described above (see MATERIALS AND METHODS).